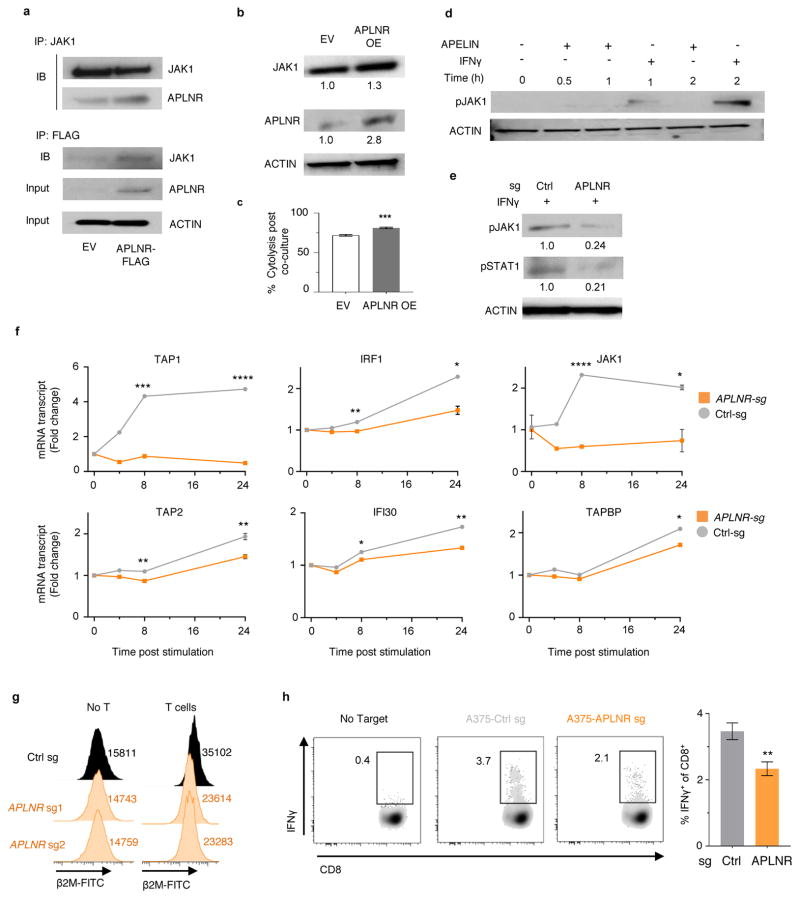
Extended Data Figure 9. APLNR modulates IFNγ signaling via physical interaction with JAK1.
a, Pull-down of JAK1 and APLNR in the extracts from HEK 293T cells transiently transfected with APLNR-FLAG plasmid. b, Immunoblot showing the upregulation of JAK1 protein expression in APLNR overexpressing A375 cells (APLNR OE). EV: Empty vector control. c, Effect of overexpression of APLNR in tumour cells on T cell-mediated cytolysis. n = 4 biological replicates. d, Immunoblot showing that addition of 100 μM Apelin ligand does not induce phosphorylation of JAK1 in tumour cells. e, Immunoblot showing the phosphorylation levels of JAK1 at Tyr1022/1023 residues and STAT1 at Tyr701 residue upon 100 ng/ml IFNγ treatment for 30 min in APLNR-edited cells versus cells receiving a control sgRNA. f, Quantitative PCR analysis of JAK1-STAT1 pathway-induced genes in APLNR-edited cells post 4, 8 and 24 h of treatment with 1 μg/ml IFNγ. n = 3 biological replicates. g, Induction of surface expression of β2M on APLNR-edited cells upon co-culture with ESO T cells for 6 h as measured by FACS. h, Intracellular staining assay performed on CD8+ T cells to measure IFNγ production post co-culture with A375 cells as target for 5–6 hr. n = 3 biological replicates. All data are representative of at least two independent experiments. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. of replicate measurements. **** P < 0.0001, *** P < 0.001 **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05.