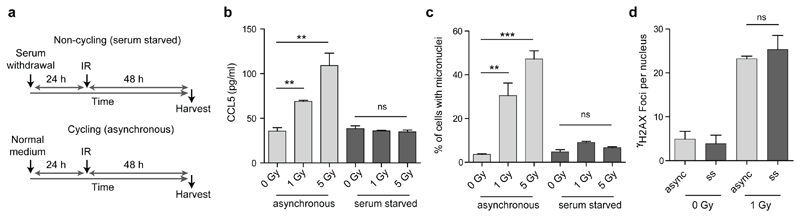
Fig 4. Innate immune activation after radiation induced DNA damage is cell cycle dependent.
(a) Schematic of experimental protocol. (b) CCL5 production is significantly increased after IR for cycling (asynchronous) cells, but not for cells arrested in G0 after serum starvation. (c) Micronuclei levels are elevated after IR in cycling but not G0-arrested cells. Mean ± SEM, n=3 independent experiments. (d) Cycling and G0-arrested cells exhibit the same level of DNA damage as measured by γH2AX foci formation per cell. Mean ± SD, n=2 independent experiments, ≥100 cells analysed per condition per experiment. (Only 1 Gy quantified, as γH2AX foci overlapped substantially at 5 Gy, see EDF6). ** = P<0.01, *** = P<0.001, two-tailed t-test; ns = not significant.