Extended Data Figure 9. The IL-17a pathway promotes abnormal behavioral phenotypes in MIA offspring born to mice colonized with human commensal bacteria.
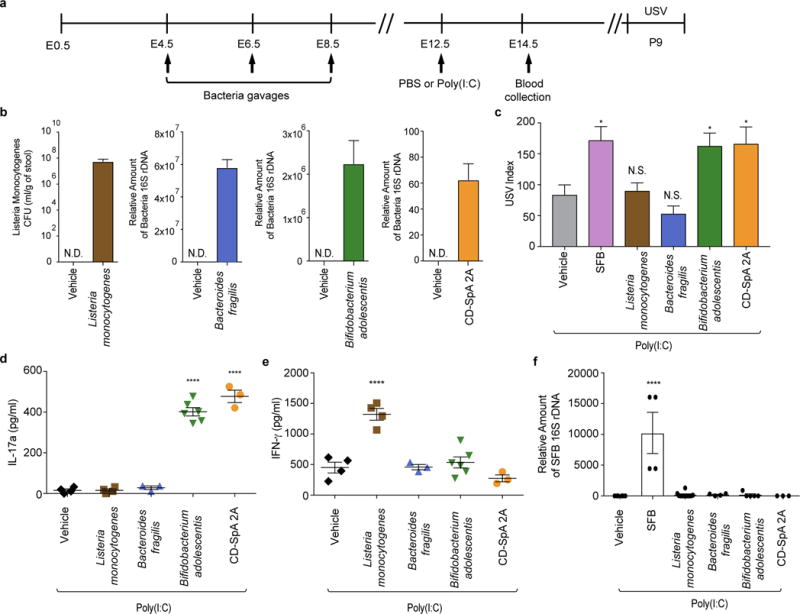
a, Schematic representation of the experimental design. b, Quantification of bacterial colonization levels through colony forming unit (CFU) counts or qPCR analyses. c, USV index (n=13/12/28/16/17/14 (poly(I:C);vehicle/SFB/Listeria monocytogenes/Bacteroides fragilis/Bifidobacterium adolescentis/CD-SpA 2A). d-e, Maternal plasma concentrations of IL-17a/IFN-γ at E14.5 (n=4/4/3/6/3 (poly(I:C);vehicle/Listeria monocytogenes/Bacteroides fragilis/Bifidobacterium adolescentis/CD-SpA 2A). f, qPCR analysis measuring relative SFB levels in Jax mice gavaged with various bacteria; from two independent experiments. *p<0.05, ****p<0.0001 as calculated by one-way (c-f) ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc tests and Student’s t-test (b). N.D., not determined. N.S., not significant. Graphs indicate mean +/− s.e.m.
