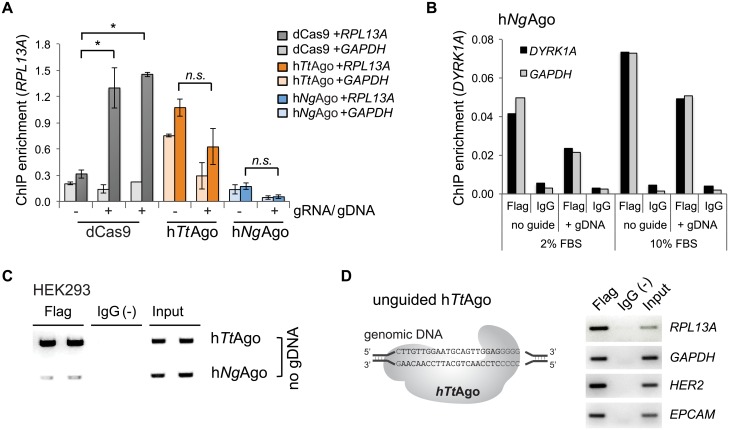
Fig 3. DNA guides do not facilitate binding of hTtAgo and hNgAgo to genomic target loci.
A. ChIP-qPCR enrichment to quantitate binding to RPL13A locus. HEK293 cells were transfected with hTtAgo- and hNgAgo-expression plasmids either with (+) or without (-) gDNAs. dCas9 and two different gRNA expressing plasmids were co-transfected as controls (Student two-sided T-test; *, p<0.05; n.s., not significant; n = 2 independent experiments; mean ± SEM). Binding to a non-target locus (GAPDH) was evaluated to interrogate binding specificity. B. Targeted binding of hNgAgo failed at the DYRK1A locus in HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were co-transfected with hNgAgo expression plasmid together with 24-nt 5’-phosphorylated gDNAs (G5 gDNA) or without gDNA. ChIP assays were performed with an antibody to the 3xFlag tag of hNgAgo or with rabbit IgG as a negative control. Addition of G5 gDNA that was targeted to the DYRK1A locus did not increase hNgAgo binding above background level (no guide). There was no difference in binding to DYRK1A or to a control region (GAPDH). Two conditions (2% or 10% FBS in growth media) were tested. C. ChIP-PCR to measure unguided hTtAgo and hNgAgo binding to the RPL13A locus. ChIP assays were performed with two biological replicates. Flag, Flag ChIP; IgG(-), IgG negative control; Input, 0.1% chromatin input. D. hTtAgo binds multiple genomic regions without gDNA in HeLa cells. ChIP assays were performed in HeLa cells expressing hTtAgo without DNA guides. Standard PCR with locus-specific primers demonstrated hTtAgo binding to RPL13A, GAPDH, HER2 and EPCAM. Flag, Flag ChIP; IgG(-), IgG negative control; Input, 0.1% chromatin input.