Figure 1.
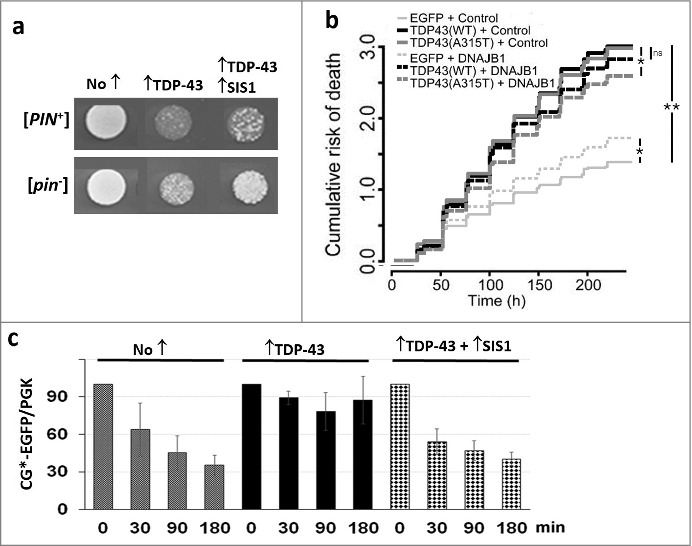
Overexpression of Sis1 mitigates the effects of TDP-43 in yeast and primary rodent cortical neurons. (Adapted from [31) a. Overexpression of TDP-43 is more toxic in the presence of the [PIN+] prion and is less toxic in the presence of overexpressed Sis1. The growth of normalized suspensions of [PIN+] and [pin−] versions of the same yeast strain transformed with pGAL1-TDP-43-YFP (↑TDP-43) and pGAL1-SIS1 (↑SIS1), or empty control plasmids (No ↑), on plasmid selective galactose medium is shown. b. Expression of DNAJB1 reduces toxicity of TDP-43 overexpression in rodent primary cortical neurons. A cumulative risk of death plot is shown for neurons transfected with vectors shown. While DNAJB1 displays some toxicity in control neurons when overexpressed, it also reduces the risk of death in neurons expressing TDP-43. *p < 0.005; **p < 2 × 10−16, by Cox proportional hazards analysis. N = 725-979 neurons per condition, assembled from three separate experiments. c. TDP-43 inhibits proteolysis of cytosolic misfolded proteins and this is reversed by overexpression of Sis1. We used degradation of CG*-GFP, the mutant version of the secretory protein carboxypeptidase Y lacking its signal sequence (ΔssCPY*) tagged with EGFP as a reporter to test for ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS) activity. New protein synthesis was inhibited with cycloheximide, after which levels of CG*-GFP were determined in cell lysates harvested at the times indicated. Data for a [PIN+] yeast strain is shown. All cells expressed CG*-EGFP from a GAL1 plasmid and expressed TDP-43 and Sis1 as indicated. Normalized cell lysates run on SDS-PAGE were immunoblotted with anti-GFP for CG*-EGFP level and anti-Pgk1 as an internal loading control. Quantification of three blots showing normalized ratio of CG*-EGFP and Pgk1 is shown with standard error.
