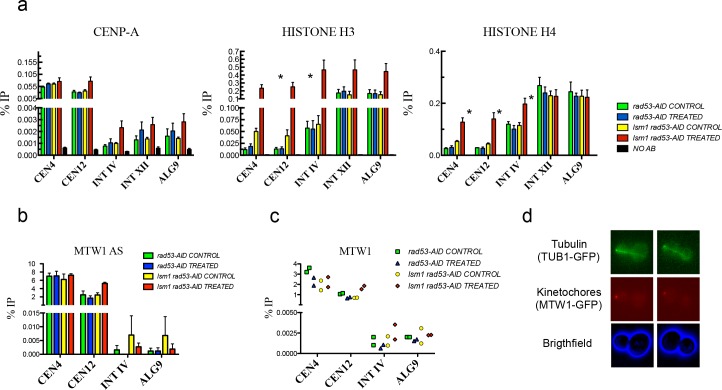
Figure 4. High levels of histones do not affect CENP-A recruitment to centromeres or the attachment of chromosomes to the spindle axis.
(a) Relative levels of histones H3, H4, Cse4 (CENP-A) measured by ChIP-Q-PCR at the indicated loci in rad53-AID (DVY22) and rad53-AID lsm1∆ (DVY23) cells. Samples were obtained from cultures treated (or not) with Auxin for 2 hr and incubated 2 additional hours with Nocodazole. CEN4 and CEN12 correspond to the centromeric region of Chromosomes IV and XII. INT IV and INT XII to intergenic regions in the same chromosomes. ALG9 corresponds to a small amplicon in the coding region of ALG9. p-Values were obtained from a Student T-test (paired samples, two tails) that compares rad53-AID-untreated cells versus rad53-AID-lsm1∆-treated cells *p<0.05. (b) MTW1 chromatin association (ChIP-qPCR) obtained in two independent experiments in which asynchronous growing rad53-AID and rad53-AID lsm1∆ cells were treated or not with NAA for 4 hr (c) Same as in b but using samples that were synchronised with NAA and Nocodazole as in (a). (d) Two representative examples of the normal distribution of kinetochores (MTW1-mCherry) along the spindle axis (Tub1-GFP) in rad53-AID lsm1∆ cells after 4 hr of Auxin treatment.