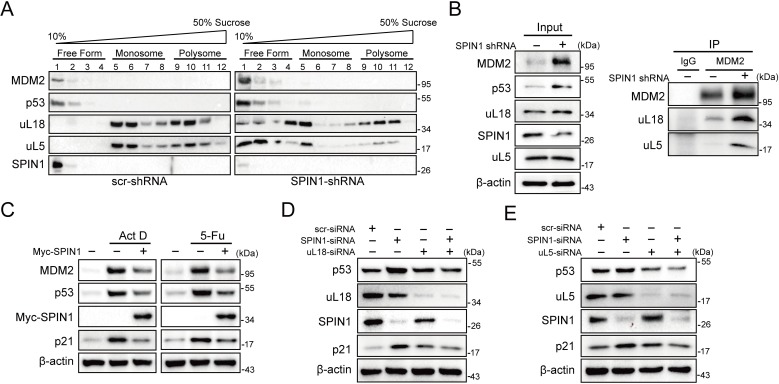
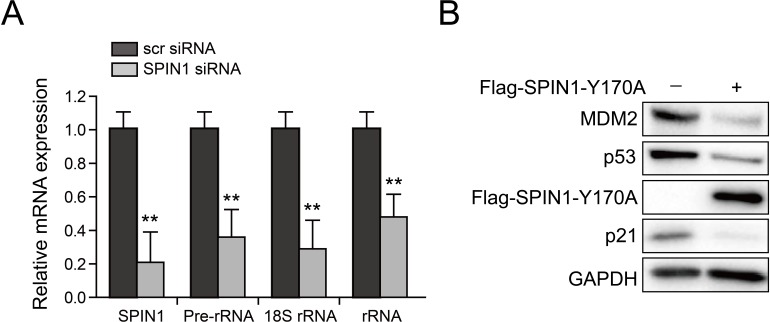
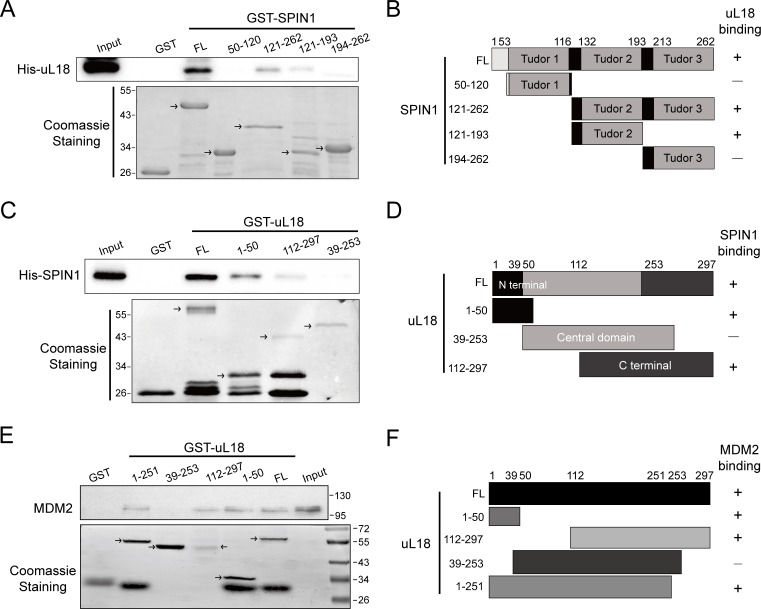
Figure 5. SPIN1 depletion increases ribosome-free uL18 and uL5.
(A) Knockdown of SPIN1 releases free forms of uL18 and uL5. HCT116p53+/+ were transfected with scramble or SPIN1 shRNA for 36 hr and subjected to sucrose gradient fractionation assay followed by WB analysis with indicated antibodies. (B) SPIN1 knockdown increases the endogenous uL18/uL5-MDM2 interaction. Cell lysates of HCT116p53+/+ cells transfected with scramble or SPIN1 shRNA were immunoprecipitated with MDM2 or control IgG, and analyzed by WB analysis with indicated antibodies. (C) SPIN1 overexpression counteracts p53 activation induced by ActD or 5-Fu. U2OS cells were transfected with pcDNA or Flag-SPIN1 for 48 hr, and treated with ActD or 5-Fu for 12 hr before harvested for WB analysis with indicated antibodies. (D) and (E) Knockdown of uL18 or uL5 compromises the induction of p53 by SPIN1 depletion. U2OS cells were transfected with scramble siRNA, SPIN1 siRNA, uL18 siRNA (D) or uL5 siRNA (E) as indicated for 48 hr. Cell lysates were subjected to WB analysis with indicated antibodies.