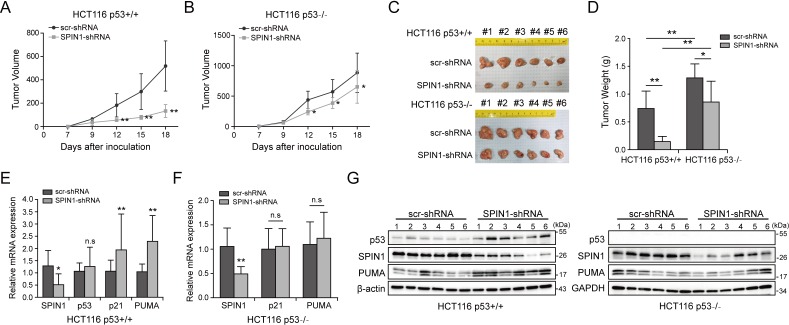
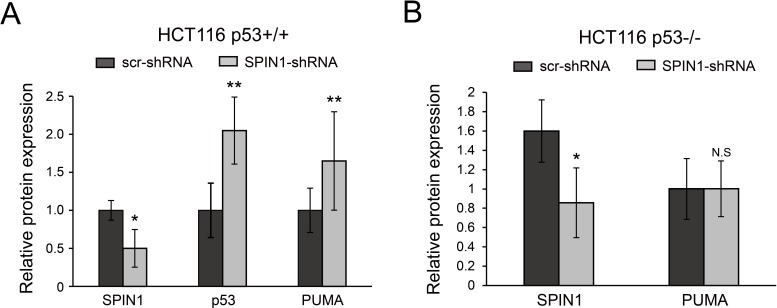
Figure 6. SPIN1 knockdown retards tumor growth more dramatically by inducing p53 activity.
(A) and (B) Growth curves of xenograft tumors derived from HCT116p53+/+ cells and HCT116p53-/- cells that expressed scramble or SPIN1 shRNA. Data are represented as mean ± SEM, n = 6. (C) The images of xenograft tumors that were harvested at the end of experiment. (D) Quantification of the average weights of collected tumors from the above experiments. (E) and (F) The mRNA levels of SPIN1, p53 and p53 target genes were detected in six tumors by RT-qPCR (mean ± SEM, n = 6). (G) The protein levels of SPIN1, p53 and p53 targets were detected in six tumors samples by WB analysis with indicated antibodies. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 by two-tailed t-test (D, E, F, G).