Fig 3. Coronary heart disease risk per standard deviation of HDL containing (red) and lacking (blue) apoC-III in strata of CVD-risk factors in four prospective studies.
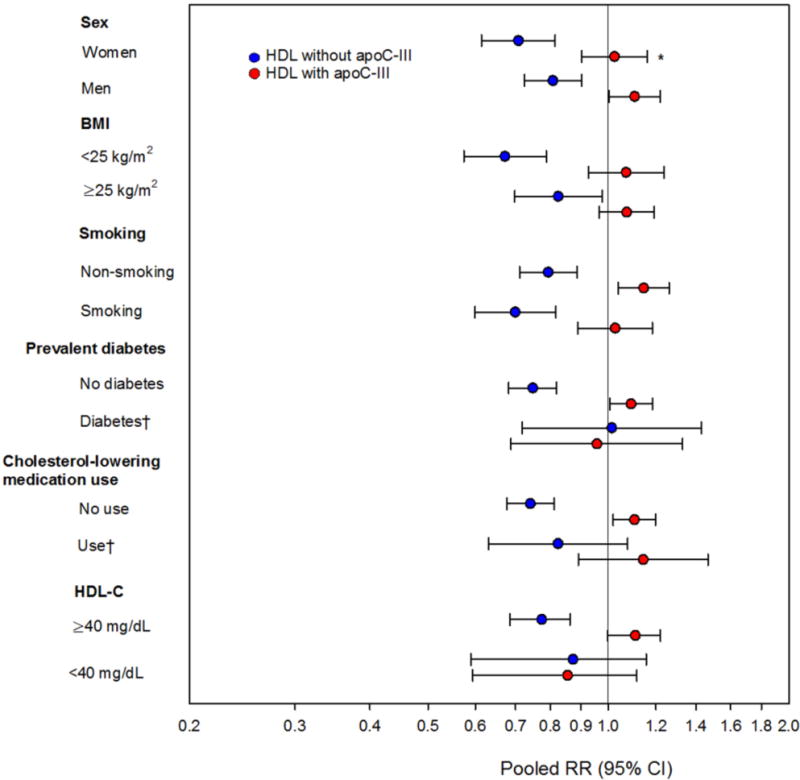
Pooled relative risks with 95% CI for risk of CHD estimated in fixed-effects meta-analysis using study-specific SDs in four prospective studies (the Diet, Cancer and Health [DCH] Study, the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis [MESA], the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study [HPFS], and the Nurses’ Health Study [NHS]). Adjusted for ASCVD (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease) risk factors: age, sex, prevalent diabetes, treatment with anti-hypertensive medication, (race/ethnicity in MESA), systolic blood pressure, smoking, and total cholesterol.
Both subtypes of HDL (containing and lacking apoC-III) are simultaneously included in all models.
*Between-study heterogeneity, p<0.05.
†Estimates not available in NHS and HPFS.
