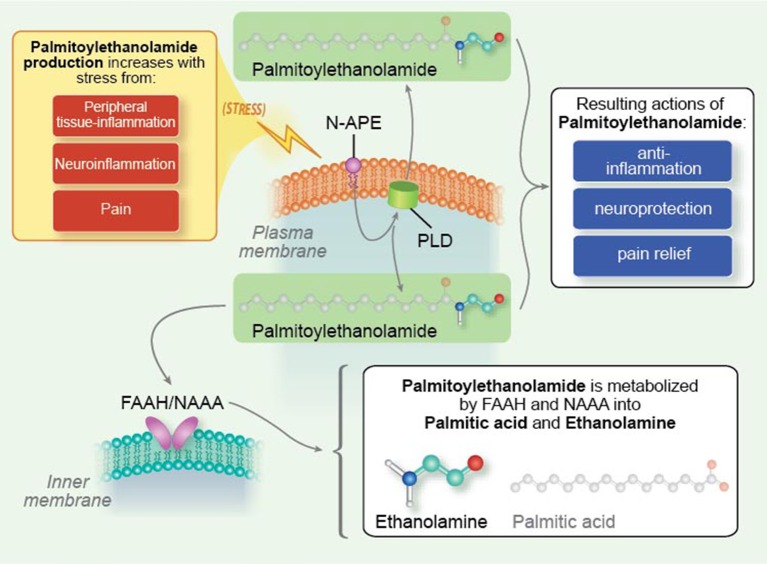
Figure 4.
Palmitoylethanolamide synthesis and metabolism. N-palmitoyl-phosphatidyl-ethanolamine (N-APE) is converted into palmitoylethanolamide and phosphatidic acid by a plasma membrane-associated N-acylated phosphatidylethanolamine-phospholipase D (PLD). Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) is broken down to palmitic acid and ethanolamine by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH, which also catabolizes other fatty acid amides) as well as the more selective N-acyl ethanolamine-hydrolyzing acid amidase (NAAA). Tissue levels of palmitoylethanolamide rise under conditions of stress, e.g., peripheral tissue inflammation, neuroinflammation, and pain [Reproduced from Skaper et al. (2014) Mast cells, glia and neuroinflammation: partners in crime? (Figure 2). Copyright © 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd. With permission].