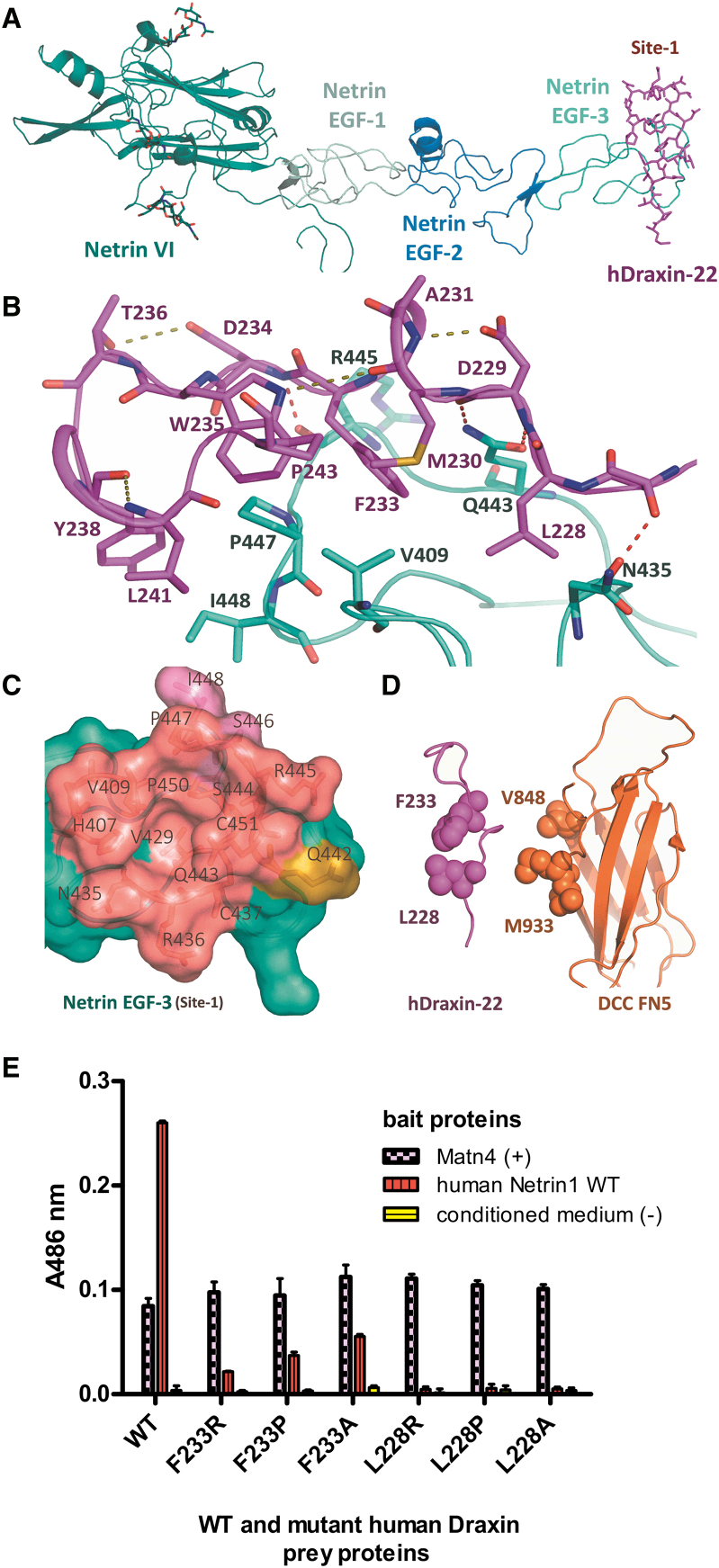
Figure 3.
Crystal Structure of the hNetrin-1/hDraxin-22 Peptide
(A) An overview of the complex showing hDraxin-22 peptide (in magenta) represented as sticks binding to the Netrin-1 on the EGF-3 domain, represented in ribbon. Netrin-1 consists of the N-terminal laminin VI domain (in deep teal), followed by three EGF domains (in pale cyan, marine, and cyan).
(B) Important residues involved in hNetrin-1/hDraxin-22 interaction interface: residues Thr227, Asp229, and Asp234 of hDraxin-22 form hydrogen bonds with Asn435, Gln443, and Arg445 of hNetrin-1, respectively, while Leu228 and Phe233 of hDraxin-22 are involved in hydrophobic interactions. The hydrogen bonds between hDraxin-22 and Netrin-1 are shown in red, while intra-Draxin hydrogen bonds are shown in deep olive.
(C) A comparison between the residues of Netrin-1 involved in Draxin and DCC binding using a surface representation of Netrin-1 site 1 located at the EGF3 domain (in cyan). The residues interacting only with Draxin are colored in pink, only with DCC are colored in olive, and with both Draxin and DCC are colored in deep salmon. These residues form a hydrophobic cavity at site 1, surrounding residue Val429 of Netrin.
(D) Comparison of the crucial residues involved in Netrin-1 binding for Draxin (Leu228 and Phe233) and DCC (Met933 and Val848).
(E) AVEXIS binding results for Netrin/WT and mutant Draxin interactions. Human Netrin-1 WT bait protein (VI+V) interacts with Draxin full-length prey proteins with indicated mutations. Matn-4 bait used as the internal positive control; conditioned medium as the negative control. The A486 nm values correspond to the average of three repeats, error bars represent mean ± SD, and results were confirmed in two independent experiments.