Figure S1.
Statistical Analysis of mPDP Experiments, Related to Figure 1
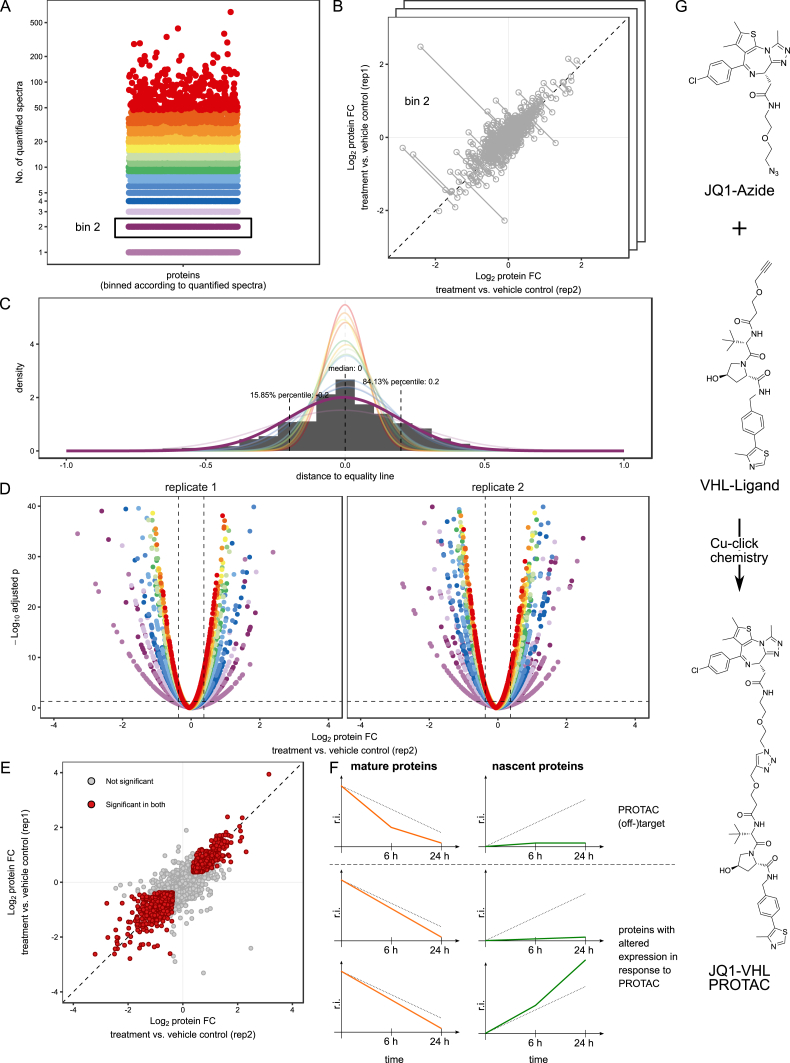
(A) Step 1: Proteins were divided into bins according to the number of quantified spectrum sequence matches (color coding according to bins). Each bin consisted of at least 300 proteins. This data quality–dependent binning strategy is analogous to the procedure described previously (see the STAR Methods).
(B) Step 2: The standard deviation per bin was calculated using robust estimation (using the 15.87, 50, and 84.13 percentiles) from the distribution of differences between the log2-transformed fold changes (FC) of the same proteins from two biological replicates divided by the square root of two:
This metric can be visualized as the distance to the unity line when plotting a scatterplot of protein log2 fold changes from two replicates. The metric measures the shortest distance to the unity line as illustrated in the figure. By using the standard deviation from the differences in log2 fold changes of proteins between two biological replicates the reproducibility between the replicates is taken into account in the statistical test. This enables to assess biologically relevant regulation upon perturbation without having to adhere to the assumption that the majority of measured proteins are not regulated.
(C) Density plots of the distance to equality line for each bin (color code according to [A]).
Step 3: For each protein log2 fold change a p value was calculated using a Z-test with a robust estimation of the standard deviation calculated in step 2. Step 2 and step3 were performed on each bin separately.
(D) Volcano plots displaying the protein fold change (FC) versus -log10 adjusted p value. Color code as in (A).
Step 4: After step 2 and 3 have been completed for all bins, adjustment for multiple hypothesis testing was performed on the full data set by using Benjamini-Hochberg correction.
(E) Scatterplots showing protein log2 fold changes (FC). Red closed circles indicate statistically significant regulation (p < 0.05) and the dashed diagonal indicates the equality line.
Step 5: Proteins were considered as significantly regulated if the following three conditions were fulfilled: (1) the adjusted p value was ≤ 0.05 in both replicates and (2) absolute protein log2 FC was greater than 0.37 in both replicates and (3) the change was in the same direction in both replicates.
(F) Schematic representation of the expected behavior of PROTAC direct targets on mature and newly synthesized proteins over time (upper panel). Expected behavior of protein indirectly affected, e.g., due to downstream effects (lower panel). Changes in protein levels are displayed as relative intensity (r.i.).
(G) Modular design of JQ1-VHL PROTAC: JQ1-Azide Cu-click chemistry reaction with VHL-Ligand to generate JQ1-VHL PROTAC.