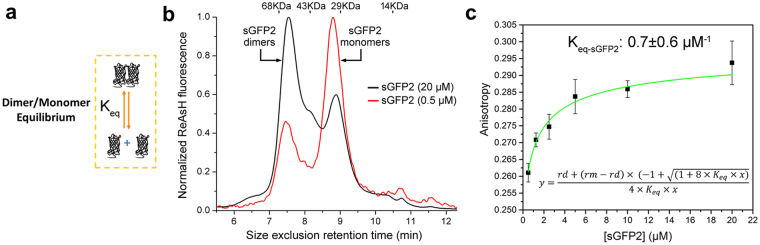
Figure 4.
Concentration-dependent dimer-monomer exchanges in recombinant split-fluorescent proteins. (a) Schematic of dimer-monomer equilibrium in recombinantly produced sFPs. Keq represents the equilibrium constant for dimer formation. (b) Size exclusion high-pressure liquid chromatography of non-complemented sGFP2 labeled with fluorescent ReAsH on an N-terminal tetracysteine tag. sGFP2 is mostly dimeric at 20 µM (apparent molecular weight of 61 KDa) but mostly monomeric at a lower concentration of 0.5 µM (apparent molecular weight of 31 KDa). The retention times of a set of calibrated molecular weight standards (68, 43, 29 and 14 KDa) are provided as reference. (c) Steady-state fluorescence anisotropy of ReAsH-labeled sGFP2 at different concentrations. The apparent equilibrium constant of dimer formation (Keq) is determined by fitting the anisotropy curve with the inset equation (green), which describes the ensemble anisotropy contributed by both dimer anisotropy (rd) and monomer anisotropy (rm) at each total sGFP2 concentration. Anisotropy values are presented as mean ± std from measurements in triplicate.