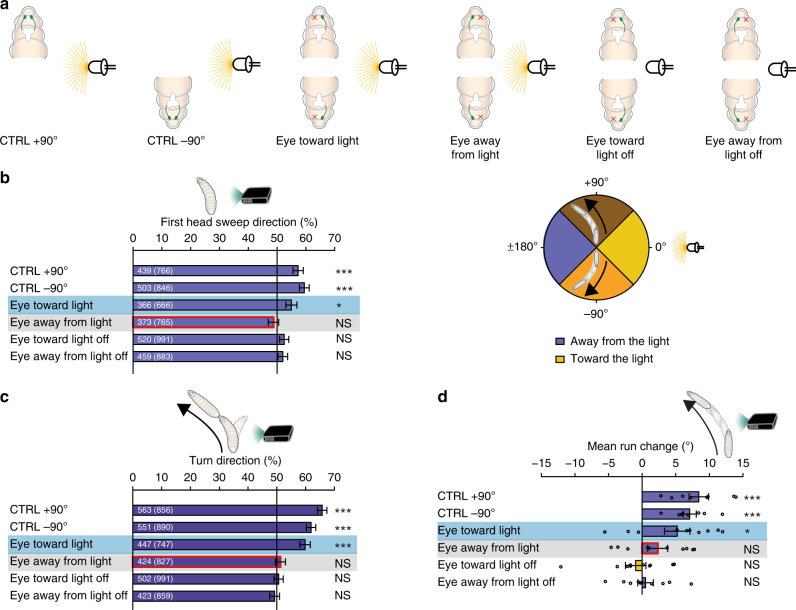
Fig. 3.
Drosophila larvae use navigational strategies based on spatial information integration to avoid a directional light source. a In dependence of heading direction is the light source on the ipsi- or contralateral side of the animal with respect to the functional eye of unilateral sensing larvae. b Heading to +90° (brown) larvae should bias their movements to the left, in order to avoid the light source. Larvae, which are orientated to −90° (orange), should bias their movements to the right to avoid the light source. Bilateral sensing animals bias their first head sweep direction away from the light source, independently of their initial heading direction. Larvae with their functional eye on the body side facing the light source bias their first head sweep direction, but not when the functional eye is on the side facing away from the light source. These animals do not bias their first head sweep to any direction in constant darkness. CTRL +90°: n = 766, p = 1.8 × 10−4; CTRL −90°: n = 846, p = 2.5 × 10−7; eye toward light: n = 666, p = 0.0234; eye away from light: n = 765, p = 0.5152; eye toward light off: n = 991, p = 0.1910; eye away from light off: n = 883, p = 0.303. c Being perpendicular to a light source, bilateral sensing animals bias their turn direction away from the light. Unilateral sensing larvae need the remaining eye on the body side toward the light, in order to bias the turn direction. CTRL +90°: n = 856, p = 1.3 × 10−15; CTRL −90°: n = 890, p = 3.6 × 10−12; eye toward light: n = 747, p = 1.7 × 10−12; eye away from light: n = 827, p = 0.7031; eye toward light off: n = 991, p = 0.7031; eye away from light off: n = 859, p = 0.7031. d Larvae steer within runs away from the light source. Unilateral sensing larvae need the functional eye facing toward the light source to bias this steering in runs. CTRL + 90°: n = 8, p = 5.2 × 10−4; CTRL −90°: n = 8, p = 5.2 × 10−4; eye toward light: n = 10, p = 0.0442; eye away from light: n = 10, p = 0.2292; eye toward light off: n = 10, p = 0.6494; eye away from light off: n = 10, p = 0.673. The data are represented as mean ± SEM. For statistical analysis the exact binomial test (b, c) and the one sample t-test (d) was applied. Benjamini Hochberg procedure was used to adjust p-values for multiple testing. Exact F-values, t-values and degrees of freedom can be found in Supplementary Table 1. b The first number gives the number of first head sweeps directed to the indicated direction (please see color code) and the number in brackets is the total number of first head sweeps in both directions. c The first number indicates the number of turns in the indicated direction and the number in brackets is the total number of turns in both directions. d Circles show means of individual experiments. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, n = not significant