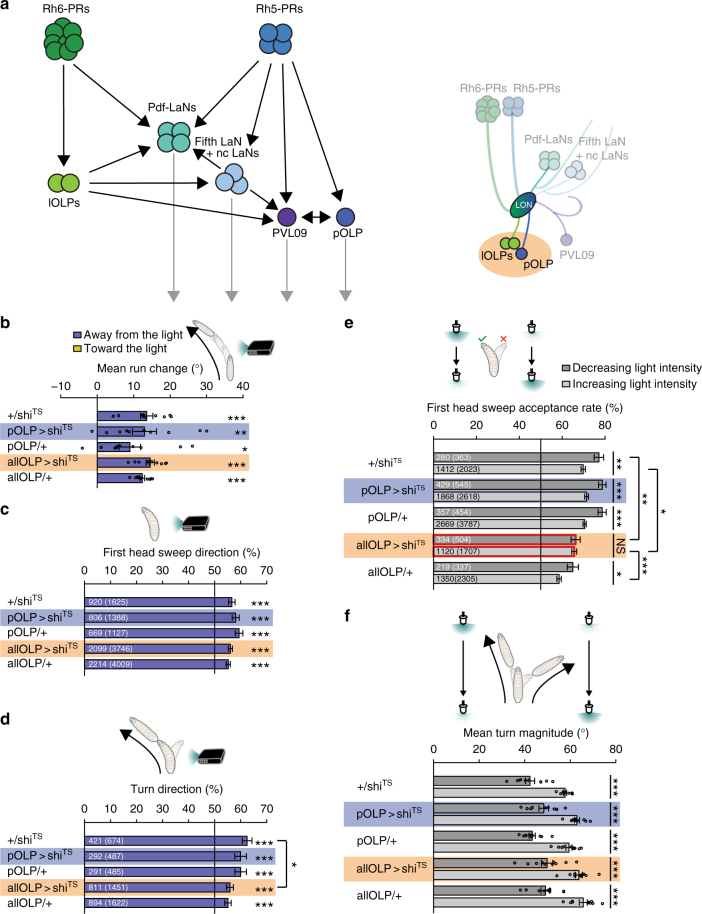
Fig. 5.
Function of the OLPs in phototaxis. a Schematic representation shows the connectome of the larval visual system. Rh5-PRs form chemical synapsis with different projection neurons. Rh6-PRs predominately make synaptic contact with the two lOLPs and the Pdf-LNs. The lOLPs form chemical synapsis with direct target cells of Rh5-PRs (adapted from ref. 28). b OLPs are not necessary to steer away from light. +/shiTS: n = 10, p = 3.9 × 10−5; pOLP > shiTS: n = 10, p = 0.0043; pOLP/+: n = 10, p = 0.0138; allOLP > shiTS: n = 10, p = 1.0 × 10−6; allOLP/+: n = 10, p = 7.5 × 10−8. Mean steering of experimental and control lines is the same. One-way ANOVA: p = 0.455. c OLPs are dispensable for biasing the first head sweep direction. +/shiTS: n = 1625, p = 1.1 × 10−7; pOLP > shiTS: n = 1388, p = 2.5 × 10−9; pOLP/+: n = 1127, p = 5.9 × 10−10; allOLP > shiTS: n = 3746, p = 8.1 × 10−13; allOLP/+: n = 4009, p = 9.8 × 10−11. The probability of the first head sweep direction is not different between experimental and control lines. pOLP > shiTS vs +/shiTS: p = 1.75; pOLP > shiTS vs pOLP/+: p = 0.687; allOLP > shiTS vs +/shiTS: p = 0.697; allOLP > shiTS vs allOLP /+: p = 0.957. d OLPs are dispensable for biasing the turn direction. +/shiTS: n = 674, p = 5.1 × 10−10; pOLP > shiTS: n = 487, p = 1.6 × 10−5; pOLP/+: n = 485, p = 1.6 × 10−5; allOLP > shiTS: n = 1451, p = 1.6 × 10−5; allOLP/+: n = 1622, p = 4.1 × 10−5. The probabilities of turning away from the light of larvae lacking functional OLPs and the effector line control is different. pOLP > shiTS vs +/shiTS: p = 0.786; pOLP > shiTS vs pOLP/+: p = 1; allOLP > shiTS vs +/shiTS: p = 0.0184; allOLP > shiTS vs allOLP /+: p = 0.9189. e Functional OLPs are necessary for accepting more first head sweeps during intensity decrease. +/shiTS: n = 2386, p = 0.0078; pOLP > shiTS: n = 3163, p = 9.9 × 10−4; pOLP/+: n = 4241, p = 9.9 × 10−4; allOLP > shiTS: n = 2211, p = 0.8308; allOLP/+: n = 2642, p = 0.0349. pOLP > shiTS vs +/shiTS (intensity decrease): p = 0.8311; pOLP > shiTS vs +/shiTS (intensity increase): p = 0.5104; pOLP > shiTS vs pOLP /+ (intensity decrease): p = 1; pOLP > shiTS vs pOLP/+ (intensity increase): p = 0.7208; allOLP > shiTS vs +/shiTS (intensity decrease): p = 0.0020; allOLP > shiTS vs +/shiTS (intensity increase): p = 0.0179; allOLP > shiTS vs allOLP /+ (intensity decrease): p = 0.8129; allOLP > shiTS vs allOLP/+ (intensity increase): p = 4.7 × 10−5. f OLPs are dispensable for making greater turns during intensity increase. +/shiTS: n = 10, p = 2.86 × 10−6; pOLP > shiTS: n = 10, p = 1.03 × 10−5; pOLP/+: n = 10, p = 6.1 × 10−7; allOLP > shiTS: n = 10, p = 1.6 × 10−4; allOLP/+: n = 10, p = 9.27 × 10−6. The mean turn magnitude delta differs not between experimental and control groups. One-way ANOVA: p = 0.818. b, f Circles are means of individual experiments. c, d The first number gives the number of first head sweeps or turns directed to the indicated direction, respectively, and the number in brackets is the total number of events. e The first number is the number of accepted first head sweeps and the number in brackets is the number of all events. b, f One sample t-test was used. c, d Exact binomial and c–e Fisher’s exact test were applied. b–f Benjamini Hochberg procedure was used. The data are shown as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, n = not significant