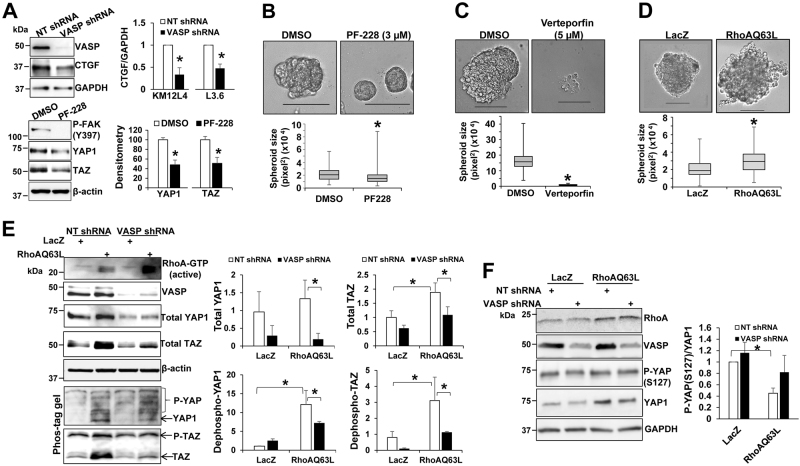
Fig. 4.
Pharmacologic targeting the β1-integrin-FAK-YAP1/TAZ signaling suppresses cancer spheroids and VASP is required for RhoA-mediated YAP1/TAZ dephosphorylation. a Upper, 3D cancer spheroids were harvested for WB for CTGF. VASP knockdown reduced CTGF protein levels in KM12L4 and L3.6 cells. *p < 0.05 by t-test, n = 3 repeats. Lower, cells on Matrigel were treated with PF–228 (3 μM) and collected for WB. PF-228 reduced YAP1/TAZ protein levels. *p < 0.05 by t-test, n = 3 repeats. Samples derived from the same experiment and gels/blots were processed in parallel. b, c PF-228 (3 μM) or Verteporfin (5 μM) reduced the size of L3.6 spheroids on Matrigel. *p < 0.05 by t-test; n > 50 per group. Bar: 100 µm. d HCT116 cells expressing LacZ (control) or RhoAQ63L were seeded on Matrigel to induce cancer spheroids. Overexpression of RhoAQ63L increased the size of cancer spheroids. *p < 0.05 by t-test; n > 50 per group. e Control and VASP knockdown cancer spheroids were harvested for regular WB and Phos-tagTM gel-based WB. RhoAQ63L increased YAP1/TAZ protein levels and YAP1/TAZ dephosphorylation in control cells and these RhoAQ63L effects on YAP1/TAZ were abrogated by VASP knockdown. Densitometry data are shown on the right. *p < 0.05 by ANOVA, n = 3. f Control and VASP knockdown cancer spheroids were harvested for WB using anti-P-YAP(S127) and YAP1. RhoAQ63L reduced the ratio of P-YAP(S127) to YAP1 and this effect of RhoA on YAP1 dephosphorylation was partially reversed by VASP knockdown. *p < 0.05 by ANOVA, n = 3. Samples derived from the same experiment and gels/blots were processed in parallel. Error bar: S.D