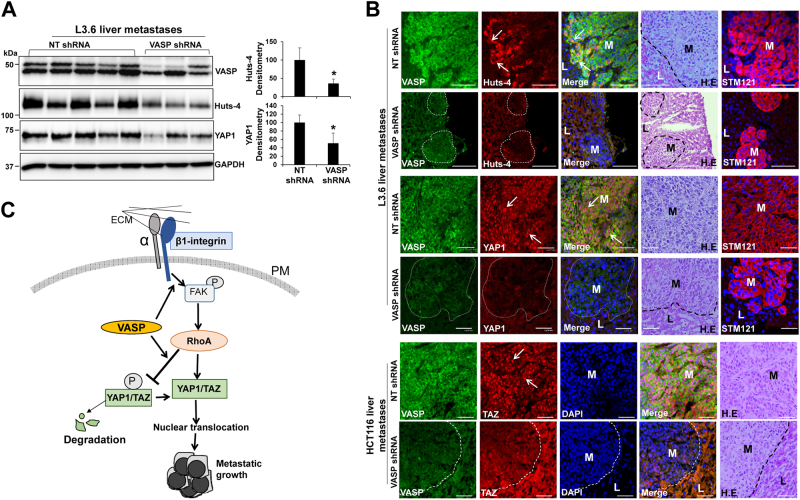
Fig. 6.
VASP knockdown suppresses β1-integrin activation and YAP1/TAZ protein levels of liver metastatic cells in mice. a L3.6 liver metastases were isolated for WB. VASP knockdown reduced Huts-4 and YAP1 levels of metastatic cells as compared to control metastatic cells. *p < 0.05 by t-test. n = 5, 3. (3 metastases were recovered from VASP knockdown group due to small tumor sizes). Samples derived from the same experiment and gels/blots were processed in parallel. Error bar: S.D. b Double IF for VASP/Huts-4 (rows 1, 2), VASP/YAP1 (rows 3, 4), and VASP/TAZ (rows 5, 6) was performed with liver biopsies. L3.6 liver metastases were identified by STEM121 IF. Cell nuclei were counterstained by DAPI. VASP knockdown markedly reduced IF signals of Huts-4, YAP1 and TAZ of metastatic cells as compared to control metastatic cells. L: liver; M: metastases. Bar, 50 µm. c VASP promotes cancer cells to colonize the liver by regulating ECM-mediated β1-integrin-FAK-RhoA–YAP1/TAZ signaling. VASP promotes this signaling pathway by two mechanisms: (1) promoting β1–integrin activation and (2) inducing YAP1/TAZ dephosphorylation at downstream of RhoA to enhance YAP1/TAZ protein abundance. PM plasma membrane, P phosphoryl group