Figure 2.
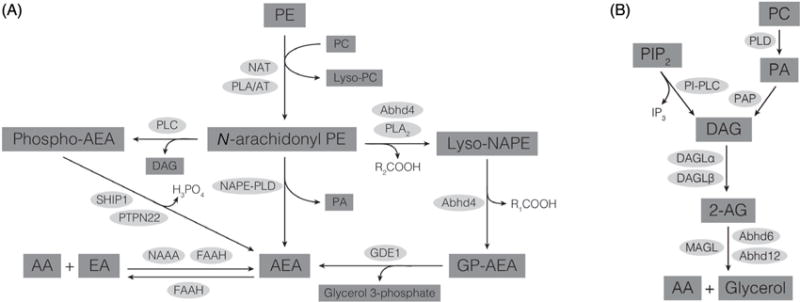
(A) Biosynthetic and catabolic pathways for AEA. (B) Biosynthetic and catabolic pathways for 2-AG. AA, arachidonic acid; Abhd, alpha-beta-hydrolase domain protein; DAG, diacylglycerol; DAGL, diacylglycerol lipase; EA, ethanolamine; FAAH, fatty acid amide hydrolase; GDE1, glycerophosphodiesterase 1; GP-AEA, glycerophospho-AEA; NAAA, N-acylethanolamine-hydrolyzing acid amidase; NAPE-PLD, N-acyl phosphatidylethanolamine-specific phospholipase D; NAT, N-acyltransferase; PA, phosphatidic acid; PAP, phosphatidic acid phosphatase; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol bis phosphate; PI-PLC, phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C; PLA/AT, phospholipase A/acyltransferase; PLA2, phospholipase A2; PLC, phospholipase C; PLD, phospholipase D; PTPN22, protein tyrosine phosphatase, nonreceptor type 22; SHIP1, Src homology 2-containing inositol phosphatase-1.
