Figure 5.
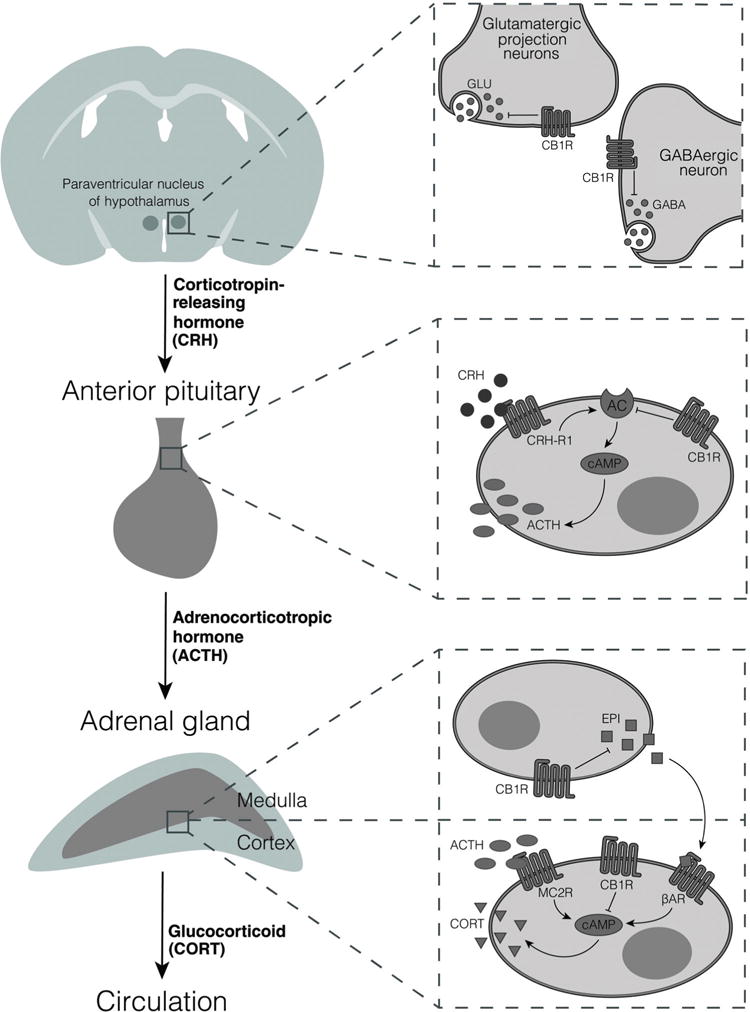
Hypothesized expression and function of CB1R along the HPA axis. Data described in the text support the expression and hypothesized inhibitory roles of the CB1R at all three levels of the HPA axis. In the paraventricular nucleus, CB1R have been identified on both glutamatergic and GABAergic terminals. Corticotropes of the anterior pituitary express CB1R, which we hypothesize, could inhibit CRH-induced activation of adenylyl cyclase (AC), thereby reducing cAMP concentrations. In the adrenal gland, CB1R have been identified on cortical cells, where we hypothesize they could oppose the elevation of cAMP induced by ACTH acting through melanocortin 2 receptors (MC2R). CB1R have also been proposed to be present on medullary cells of the adrenal gland and to inhibit the release of epinephrine (EPI) from these cells. This would result in reduced activation of ß-adrenergic receptors (ßAR) on the cortical cells.
