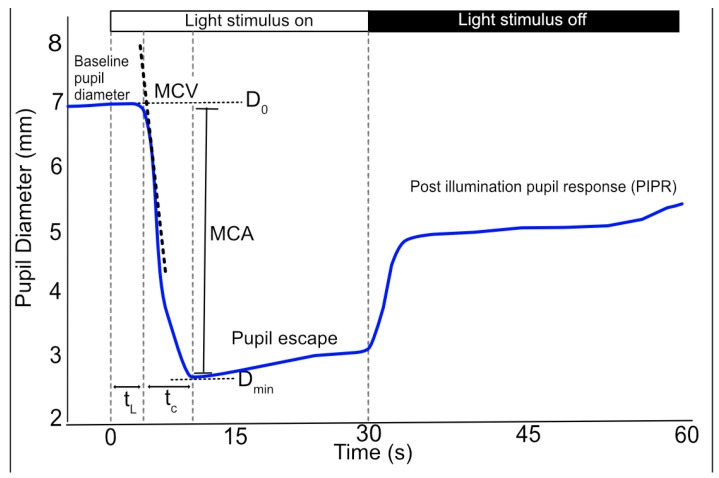
Figure 1.
Schematic of the pupillogram (blue line) and associated PLR parameters. The light stimulus at time zero results in a rapid reduction in pupil diameter. Latency (tL) is calculated as the elapsed time between light onset and the start of constriction. The pupil then rapidly constricts (maximal constriction velocity; MCV) from the baseline (D0) pupil diameter to the minimum (Dmin) pupil diameter; the constriction time (tC) and maximum constriction amplitude (MCA) are calculated as the time interval and size difference between these two values, respectively. At offset of light stimulus or during sustained light stimulation the pupil undergoes a period of rapid redilation or pupillary “escape” to a partially constricted state. Subsequently the pupil slowly returns to the baseline diameter.