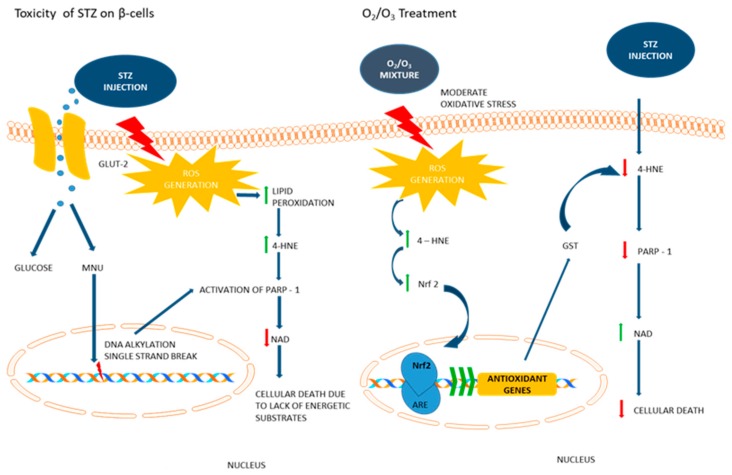
Figure 9.
Proposed mechanism of ozone activity in STZ rats. Left panel: STZ induces increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, lipid peroxidation, accumulation of 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) and DNA fragmentation; consequently, PARP-1 levels are increased in order to attempt DNA repair. Right panel: oxygen/ozone administration promotes a moderate oxidative preconditioning state, which in turn is able to increase Nrf2, GST production and anti-oxidative defense mechanisms. 4-HNE, PARP-1 and cellular death are decreased, this reduction resulted in higher levels of insulin and leptin and consequently improved the glycemia.