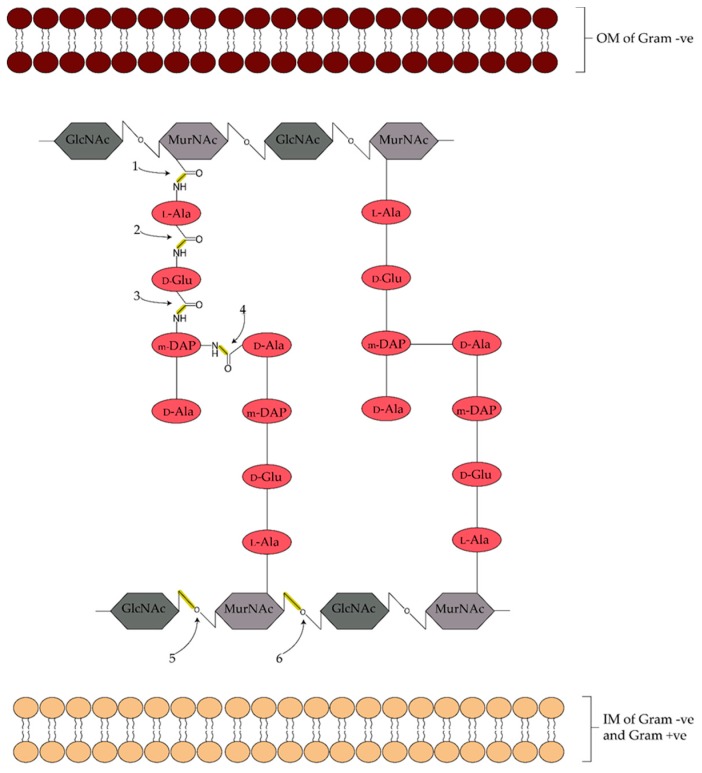
Figure 2.
Diagram of the typical cell wall and peptidoglycan structure of bacteria, including the endolysin cleavage sites. The peptidoglycan is composed of repeating sugar units, N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) and N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc), which are cross-linked via an interpeptide bridge between the meso-diaminopimelic acid (m-DAP) and d-alanine (d-Ala) residues of adjacent tetrapeptide chains. The chains also contain L-alanine (l-Ala) and D-glutamic acid (d-Glu). Gram-negative bacteria contain an outer membrane (OM) structure not present in Gram-positive bacteria. Both contain an inner membrane (IM) structure. The cleaved bonds and major classifications of endolysin are indicated: (1) N-acetylmuramoyl-l-alanine amidase; (2–4) various endopeptidases; (5) N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase; (6) N-acetyl-β-d-muramidase (lysozyme).