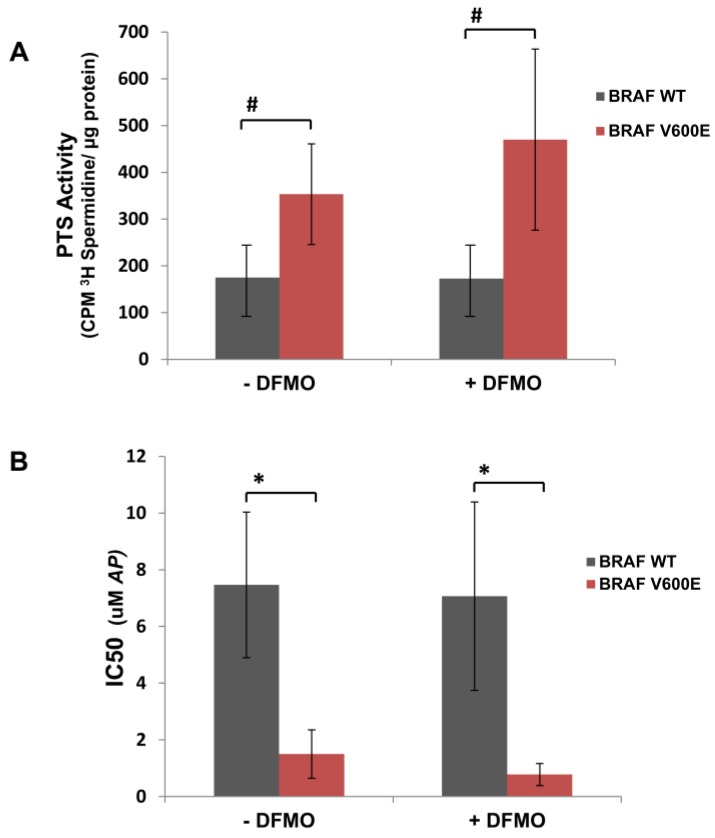
Figure 2.
Greater PTS activity and increased sensitivity to AP in mutant BRAFV600E human melanoma cells compared to wild type (WT) BRAFWT cells. (A) BRAFV600E human melanoma cells (WM983B, WM3734, 1205Lu, WM989, and WM88) and BRAFWT human melanoma cells (WM3451, WM3743, and WM3211) were cultured with and without 1 mM DFMO for 40 h and then pulsed with 0.5 µM 3H-spermidine for 60 min at 37 °C. Cell lysates were assayed for CPM 3H-spermidine per mg protein by scintillation counting. The mean PTS activity ± SD for BRAFWT melanoma cells is compared with that of BRAFV600E melanoma cells under conditions where cells were cultured without added DFMO or with 1 mM DFMO. (B) BRAFV600E human melanoma cells (WM983B, WM3734, 1205Lu, WM989, and WM88) and BRAFWT human melanoma cells (WM3451, WM3743, and WM3211) were treated with increasing doses of AP with or without 1 mM DFMO, using 5–6 samples per dose of AP. After 72 h of culture, cell survival was determined via EZQuant Cell Quantifying assay (Alstem, Richmond, CA, USA). AP IC50 values were calculated by GraphPad Prism 6. The mean AP IC50 values ± SD for BRAFWT melanoma cells is compared with that of BRAFV600E melanoma cells under conditions where cells were cultured without added DFMO or with 1 mM DFMO; # p ≤ 0.05; * p < 0.01.