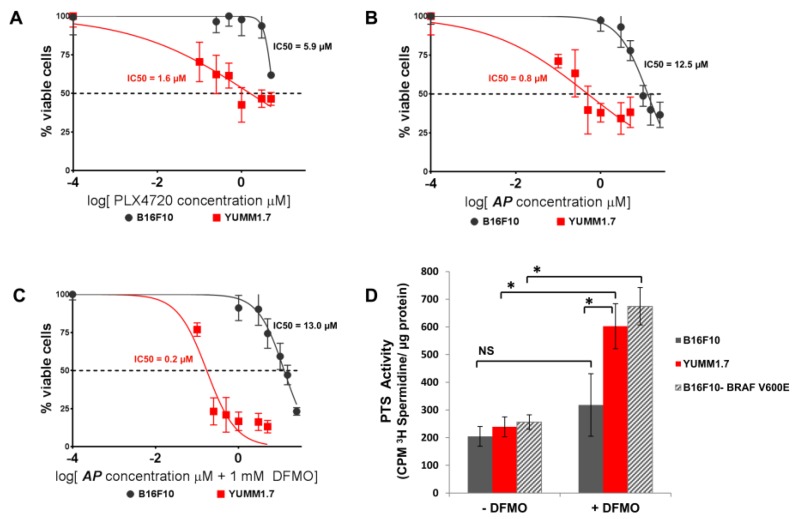
Figure 3.
BRAFV600E murine melanoma cells are more sensitive to AP than BRAFWT melanoma cells. (A) Murine BRAFV600E YUMM1.7 melanoma cells and BRAFWT B16F10 melanoma cells were treated with increasing doses of PLX4720. After 72 h of culture, cell survival was determined via EZQuant Cell Quantifying assay. IC50 values were calculated by GraphPad Prism 6; p = 0.0013. (B) Murine BRAFV600E YUMM1.7 melanoma cells and BRAFWT B16F10 melanoma cells were treated with increasing doses of AP. After 72 h of culture, cell survival was determined via EZQuant Cell Quantifying assay. IC50 values were calculated by GraphPad Prism 6; p < 0.0001. (C) Murine BRAFV600E YUMM1.7 melanoma cells and BRAFWT B16F10 melanoma cells were treated with increasing doses of AP ± 1 mM DFMO. After 72 h of culture, cell survival was determined via EZQuant Cell Quantifying assay. IC50 values were calculated by GraphPad Prism 6; p < 0.0001. (D) YUMM1.7 and B16F10 melanoma cells and B16F10 cells retrovirally infected to express the mutant BRAFV600E protein were cultured with and withoutS 1 mM DFMO for 40 h and then pulsed with 0.5 µM 3H-spermidine for 60 min at 37 °C. Cells were washed with cold PBS containing 50 µM spermidine, and cell lysates were assayed for CPM 3H-spermidine per mg protein by scintillation counting; * p < 0.0001; NS: not significant.