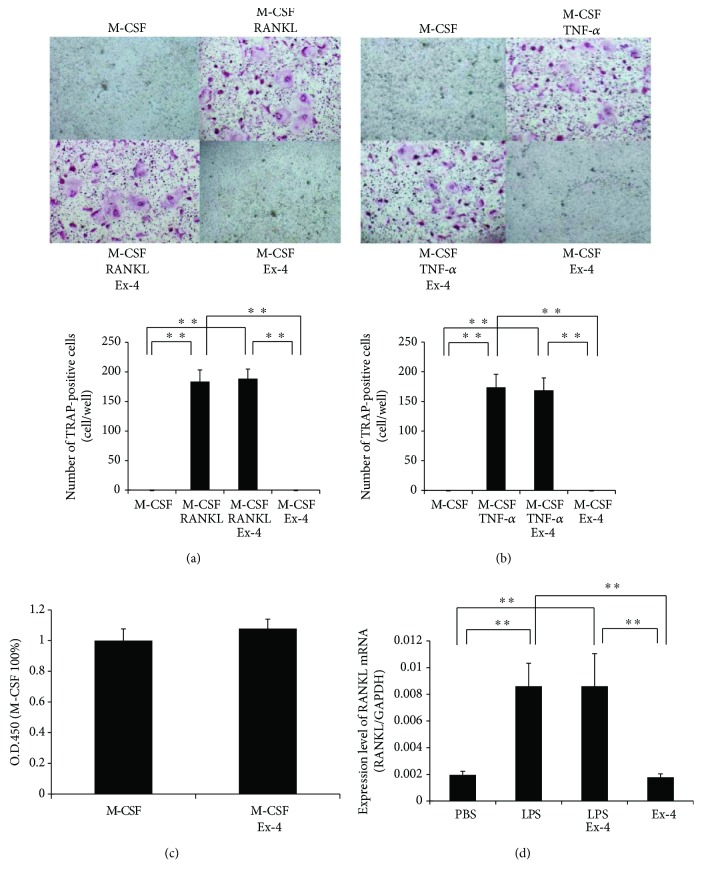
Figure 4.
Exendin-4 had no effect on RANKL-induced osteoclast formation, TNF-α-induced osteoclast formation, osteoclast precursor cell viability, or LPS-induced RANKL expression in stromal cells in vitro. (a) Microscopic images and numbers of TRAP-positive cells. Osteoclast precursors were treated with macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) alone, M-CSF with RANKL, M-CSF with RANKL and exendin-4, and M-CSF with exendin-4 for 5 days, then stained with TRAP solution. (b) Microscopic images and numbers of TRAP-positive cells. Osteoclast precursors were treated with M-CSF alone, M-CSF with TNF-α, M-CSF with TNF-α and exendin-4, and M-CSF with exendin-4 for 5 days, then stained with TRAP solution. (c) Cell viability of osteoclast precursor cells treated with M-CSF alone and M-CSF with exendin-4 for 5 days. Cell viability was determined by cell counting kit-8. Data is presented as percentage activity relative to the activity in the culture with M-CSF alone and is expressed as means ± SD. (d) RANKL mRNA expression levels in stromal cells determined by real-time RT-PCR method. Total RNA was extracted from stromal cells that were cultured with PBS, LPS with or without exendin-4, and exendin-4 alone, respectively. RANKL mRNA levels were normalized to that of GAPDH. Statistical significance of differences was determined by Scheffe's test (n = 4; ∗∗P < 0.01).