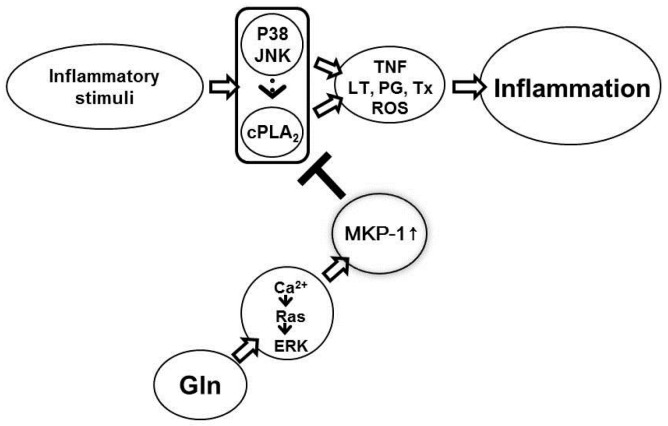
Figure 5.
Anti-inflammatory action mechanisms of Gln. Gln binds to G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), an allosteric receptor, (unpublished data), and increases ERK activity via activation of the pathway involving Ca2+/Ras/c-Raf/MEK (ERK cascade) [41]. ERK phosphorylates MKP-1 on two carboxyl-terminal serine residues—serine 359 and serine 364, which enhances MKP-1 stabilization, resulting in the early induction of MKP-1 [20]. MKP-1 deactivates cPLA2 either by dephosphorylating p38 [20,23], which is a major upstream pathway for cPLA2 phosphorylation, or by directly dephosphorylating cPLA2 due to enhanced physical interaction between Gln-induced MKP-1 and cPLA2 [24]. Deactivation of p38 and cPLA2 results in suppression of many cardinal inflammatory mediators including reactive oxygen species.