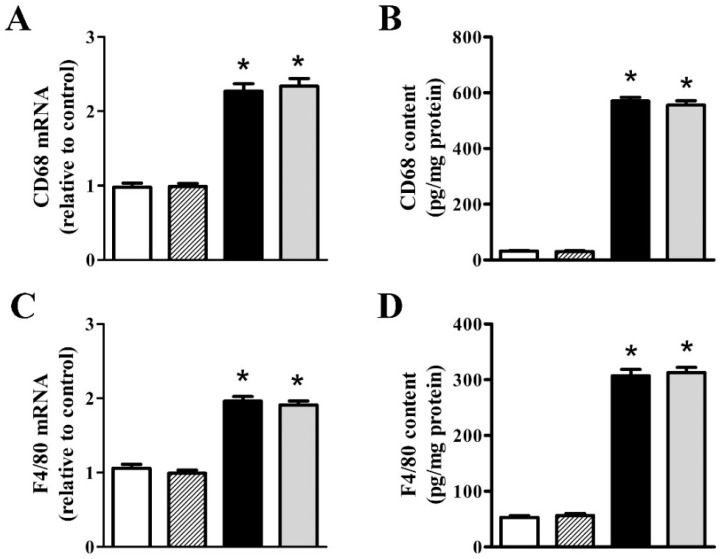
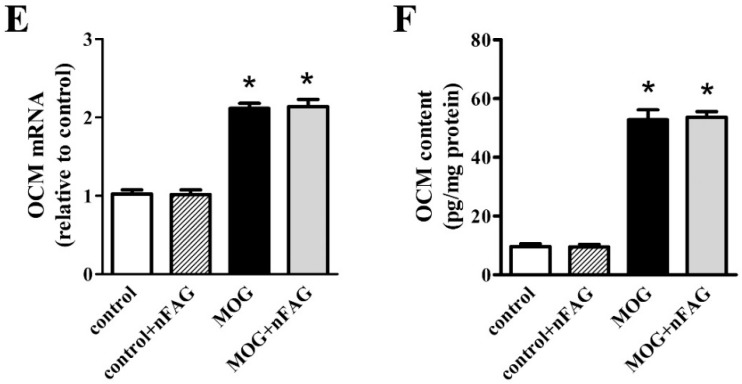
Figure 4.
nFAG dietary supplementation does not affect MOG-induced upregulation of markers of macrophage infiltration including cluster of differentiation 68 (CD68; A,B) and endothelial growth factor-like module-containing mucin-like hormone receptor-like 1 (F4/80; C,D), as well as the expression and the content of oncomodulin (OCM; E,F). Levels were evaluated in control and MOG-treated mice, without or with nFAG dietary supplementation. Transcripts (A,C,E) were evaluated by relative quantification with qPCR. Data were analyzed by the formula 2−ΔΔCT using Rpl13a as the internal standard. Proteins (B,D,F) were evaluated by ELISA (LifeSpan Biosciences, Inc., Seattle, WA, USA). Data are shown as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 9 for each experimental group). * p < 0.001 versus control (one-way ANOVA followed by the Newman-Keuls multiple comparison post-hoc test). White bars, control mice; dashed bars, control mice with nFAG dietary supplementation; black bars, MOG-treated mice; grey bars, MOG-treated mice with nFAG dietary supplementation.