Table 1. Evaluating reaction conditions for directed C–H bromination.
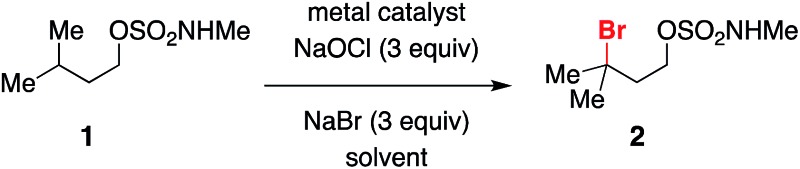
| |||
| Entry | Catalyst | Solvent a | [2]/[1] b |
| 1 | (R,R)-Mn-Jacobsen (5%) | CH2Cl2 | RSM |
| 2 | Co(OAc)2·4H2O (5%) | CH2Cl2 | 1/8 |
| 3 | CuBr2 (5%) | CH2Cl2 | 1/8 |
| 4 | Ni(OAc)2·4H2O (5%) | CH2Cl2 | RSM |
| 5 | Rh 2 (oct) 4 (5%) | CH 2 Cl 2 | 4/1 |
| 6 | Rh2(O2CtBu)4 (5%) | CH2Cl2 | 2/1 |
| 7 | Rh 2 (O 2 CCPh 3 ) 4 (5%) | CH 2 Cl 2 | 4/1 |
| 8 | Rh2(OAc)4 (5%) | CH2Cl2 | 1/5 |
| 9 | Na4Rh2(CO3)4 (5%) | CH2Cl2 | 1/7 |
| 10 | None | CH2Cl2 | 1/4 |
| 11 | None c | CH2Cl2 | RSM |
| 12 | Rh2(oct)4 (5%) | CH2Cl2 d | 1/3 |
| 13 | Rh2(oct)4 (5%) | CH2Cl2 e | 1/2 f |
| 14 | Rh2(oct)4 (5%) | iPrOAc | 1/2 |
| 15 | Rh2(oct)4 (5%) | Benzene | 1/2 |
aAll reactions were performed in a biphasic solvent mixture with the indicated solvent and an equivalent volume of saturated aqueous Na2HPO4 unless otherwise noted.
bProduct ratio determined by 1H NMR integration, see ESI for details.
cReaction flask wrapped in foil.
dReaction performed with no added co-solvent.
eReaction conducted with an equivalent volume of deionized H2O.
fA small amount of the corresponding chloride product is also formed. RSM = recovered starting material.
