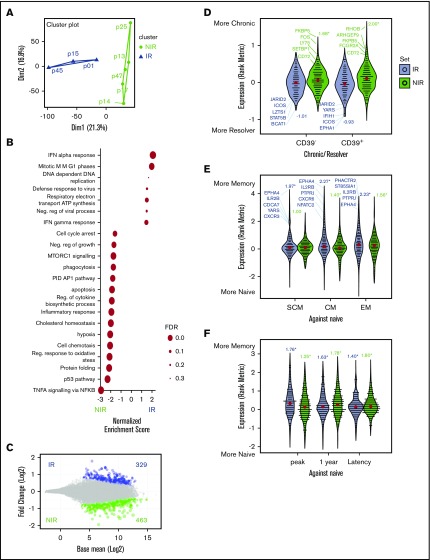
Figure 2.
Identification and characterization of gene signatures associated with reactive and nonreactive CMV+ lymphocytes. (A) Similarities between the transcriptome profiles of CMV-specific memory CD8+ lymphocytes from HSCT recipients were assessed using PCA, with NIR recipients in green and IR recipients in blue. (B) Enrichment of functional gene sets at either ends of the gene expression spectrum from more in NIR to more in IR T cells. (C) Gene expression differences in T cells from IR and NIR recipients, with significantly (false discovery rate [FDR] <0.2) different genes colored blue (IR) or green (NIR). (D-F) Expression of the IR (blue) and NIR (green) signature genes in (D) T cells from chronic HCV vs resolved HCV patients, (E) CD8 memory subsets (stem cell memory [SCM], central memory [CM], and effector memory [EM]) and (F) different stages of CMV infection. Expression assessed by rank metric (weighted signal to noise) with median values shown in red. Normalized enrichment score shown. *P < .05. Values in panel C incorporate zero-centered normal priors, and thus, shrinkage was greater for the log2-fold change estimates from genes with low counts, and high dispersion and points are sized according to their P value. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; PID, Pathway Interaction Database; TNFA, tumor necrosis factor alpha.