Fig. 1.
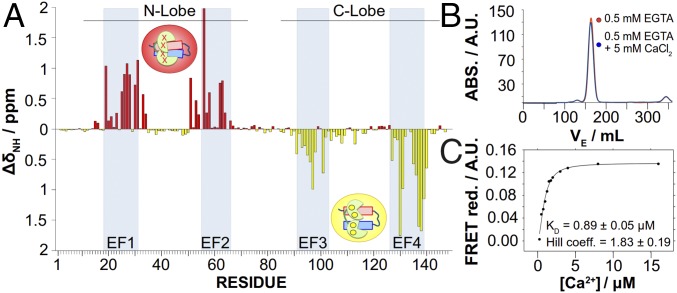
CSPs induced by Ca2+ over CaM complexed with helices A and B. (A) CSP analysis of residues forming CaM. The apoCaM/Kv7.2-hAB complex shows large CSPs in the EF1 and EF2 hands, whereas holoCaM/Kv7.2-hAB shows large CSPs in the EF3 and EF4 hands, demonstrating that intCaM/Kv7.2-hAB is Ca2+-loaded in the N-lobe, whereas the C-lobe is Ca2+-free. ΔδNH, absolute amide chemical shift differences. (B) Size exclusion chromatography profiles after injecting samples with and without Ca2+ in a Superdex 26/60 column. Elution peaks for the apo- and holoCaM/Kv7.2-hAB complexes (30.27 kDa) are almost identical (162.66 mL and 163.896 mL, respectively), corresponding to a theoretical molecular mass of 31.13 kDa and 30.3 kDa, respectively. ABS., absorbance; VE, eluted volume. (C) Ca2+ titration curve for the CaM/Kv7.2-hAB complex. Ca2+ affinity is measured by FRET ratio reduction between the mTFP1 (donor) and mVenus (acceptor) fluorophores located in the N and C termini of the Kv7.2-hAB construct complexed with CaM. The EC50 value (equivalent to an apparent Kd for the C-lobe) is 0.89 ± 0.05 μM, and the Hill coefficient is h = 1.83 ± 0.19 as obtained from the fitting to a Hill equation: where EC50 corresponds to the concentration of Ca2+ at which FRET change is half-maximal, h is the Hill coefficient, and is the FRET change found at a large excess of free calcium.