Figure 5.
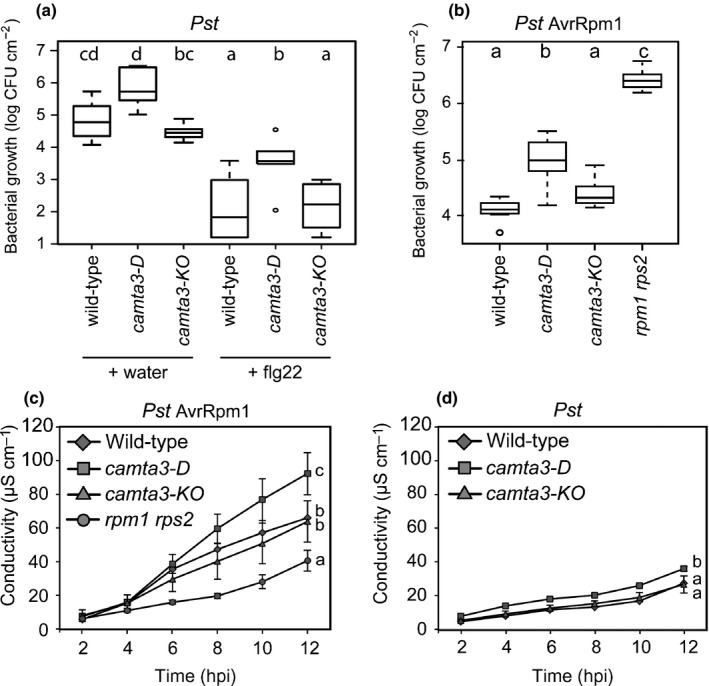
A dominant camta3 mutation compromises flg22‐ and RPM1‐mediated disease resistance, but enhances host cell death response on pathogen challenges in Arabidopsis thaliana. (a) Bacterial growth at 2 d after infiltration of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato (Pst) DC3000 (OD 600 = 0.0001). flg22 (1 μM) or water was infiltrated 24 h before Pst infiltration. (b) Bacterial growth at 3 d after infiltration of Pst expressing AvrRpm1 (OD 600 = 0.0001). (a, b) Boxplots summarize the observed log10‐transformed bacterial counts. Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05; ANOVA with Tukey post‐hoc tests). CFU, colony‐forming unit; OD, optical density. Two independent experiments with two (a, b for camta3‐KO with Pst AvrRpm1) or three replicates per experiment were conducted. (c, d) Ion leakage assays on bacterial pathogen challenge. Samples were collected at 0.5 h post‐infiltration (hpi) with Pst (OD 600 = 0.05) expressing (c) or lacking (d) AvrRpm1. Data were obtained in three independent experiments (n = 5) for the avirulent and two independent experiments (n = 4) for the virulent pathogen challenge. Means ± SE are shown. Different letters next to the lines indicate significant differences in ion leakage between genotypes (P < 0.05; ANOVA with Tukey post‐hoc tests; data at 2 and 4 hpi are excluded). (a–d) camta3‐D and camta3‐KO indicate a dominant camta3 mutant carrying an A855V substitution and a knockout camta3 mutant, respectively.
