Figure 1.
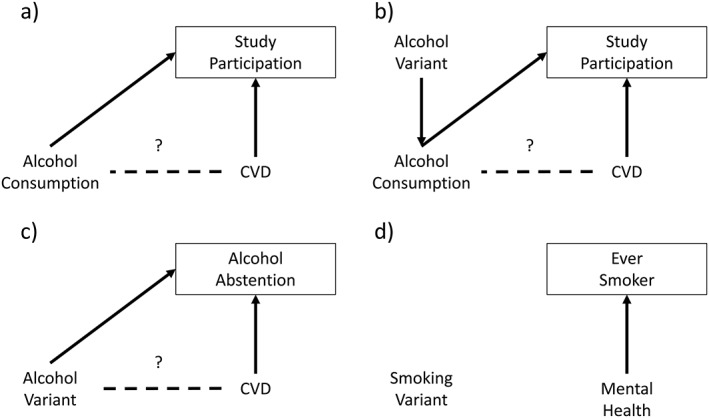
Directed acyclic graphs illustrating collider bias. (a) Collider bias within a traditional observational study arising from sample selection. The box around study participation indicates stratification on this variable. As study participation is influenced by both alcohol consumption and cardiovascular disease (CVD), stratification induces an association between these variables, indicated by the dashed line. (b) Mendelian randomization study which is still subject to collider bias. (c) Abstention is influenced by the genetic variant and the health outcome, inducing collider bias when stratifying by abstention. (d) The genetic variant is not associated with whether someone ever becomes a smoker, so there is no collider bias when stratifying on smoking status
