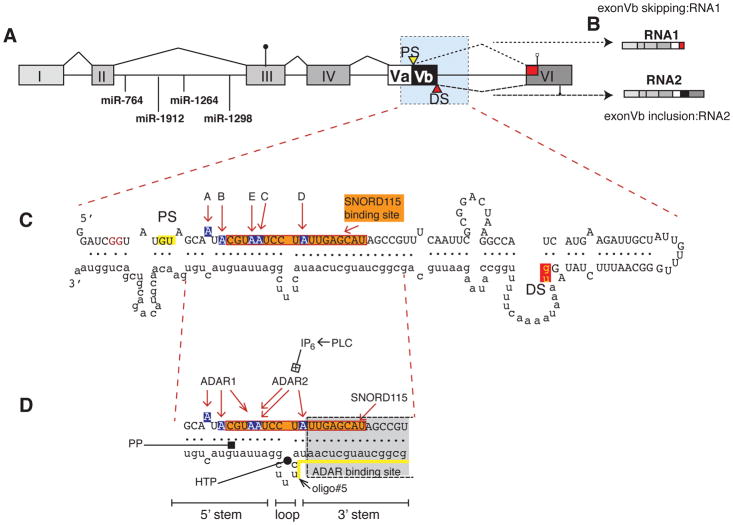
Figure 1. Gene structure and regulation of the 5HT2C pre-mRNA.
A. Gene structure of the serotonin receptor 2C. PS, DS: proximal and distal splice sites. The start codon in exon III is indicated by a circle, the two stop codons in exon VI by open and filled squares. The blue shaded area forms the dsRNA structure shown in C. The location of the miRNAs in intron II is indicated.
B. The exon structure of RNA1 and RNA2 generated through alternative splicing of exon Vb is indicated.
C. dsRNA structure formed by exon Vb and Intron V. A–E indicate the sites changed by deamination. The binding site for SNORD115 is boxed in orange. Blue nucleotides depict the five adenosine residues (A–E) that can be deaminated to inosines. The first two nucleotides of the proximal and distal 5′ splice sites (gu) are highlighted in yellow and red.
D. Site of regulation in the ds RNA structure. PLC: phosphor lipase C, IP6: hexakisphosphate. HTP: helix threading peptide binding to the central loop (Schirle et al. 2010), PP: pyrvinium pamoate (Shen et al. 2013); oligo#5: binding site for splice site changing oligo, indicated by a yellow line (Zhang et al. 2016). The SNORD116 binding site is indicated by an orange box, and adenosines shown in blue indicate the editing sites.