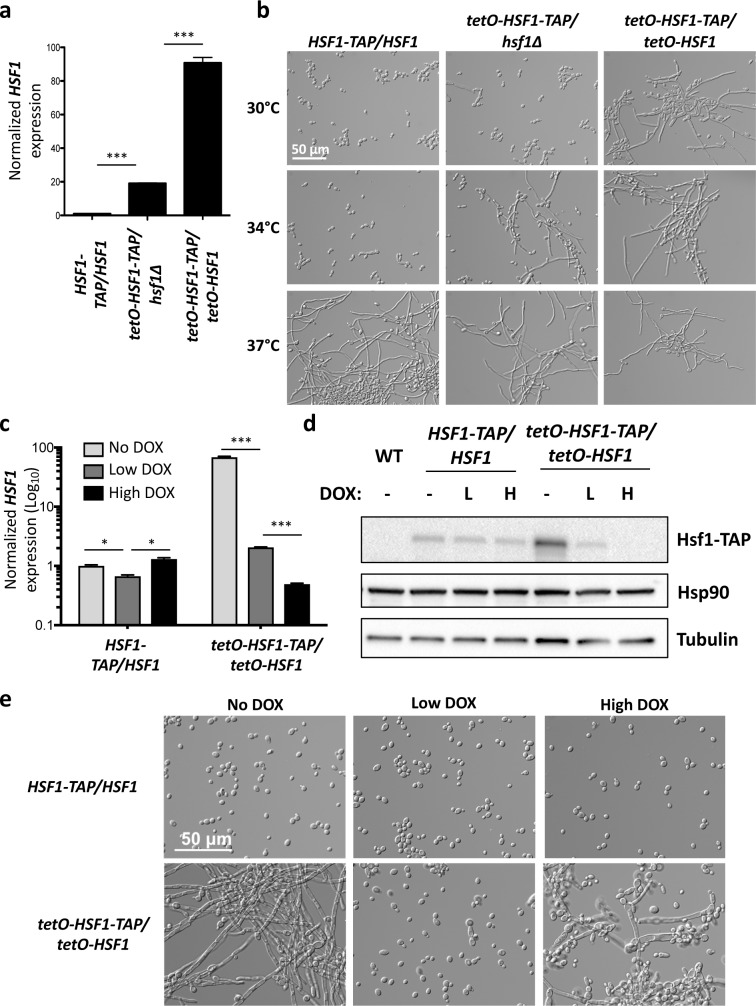
Fig 1. Overexpression or depletion of HSF1 induces filamentation.
a) HSF1 levels can be overexpressed to different levels by placing one or both alleles of HSF1 under the control of the tetracycline-repressible promoter, tetO. Strains were grown in the absence of doxycycline (DOX) to mid-log phase. HSF1 transcript levels were measured by quantitative RT-PCR and normalized to ACT1 and GPD1. Data are means +/- standard error of the means for triplicate samples. *** indicates P value <0.005, unpaired t test. b) Overexpression of HSF1 can bypass the temperature requirement for morphogenesis. Strains were grown in the absence of DOX for 4 hours at the indicated temperature. c) The tetO-HSF1-TAP/tetO-HSF1 strain can be used to monitor the effect of both HSF1 overexpression and depletion. HSF1 is overexpressed in the tetO-HSF1-TAP/tetO-HSF1 strain when grown in the absence of DOX (No DOX). HSF1 expression is lowered when the strain is grown in the presence of 0.1 μg/mL DOX (Low DOX), and is depleted when grown with 20 μg/mL DOX (High DOX). HSF1 transcript levels were measured by quantitative RT-PCR and were normalized to ACT1 and GPD1. Data are means +/- standard error of the means for triplicate samples and are graphed on a log10 scale. *** indicates P value <0.005, * indicates P value <0.05, unpaired t test. d) Hsf1 protein levels are overexpressed when the tetO-HSF1-TAP/tetO-HSF1 strain is grown in the absence of DOX, reduced when grown in 0.1 μg/mL DOX (Low DOX, labelled L), and depleted when grown in 20 μg/mL DOX (High DOX, labelled H). WT indicates the wild type, untagged control. Tubulin levels serve as loading control. e) HSF1 overexpression or depletion induces filamentation in the absence of an inducing cue. Strains were grown in the presence of no DOX, 0.1 μg/mL DOX (Low DOX), or 20 μg/mL DOX (High DOX) at 30°C.