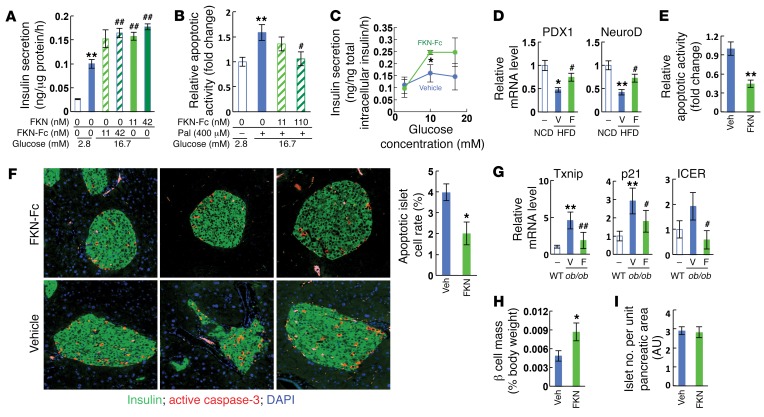
Figure 2. Chronic FKN-Fc administration enhances GSIS and decreases apoptosis in the islets of obese mice.
(A) Static GSIS in primary mouse islets. (B) Relative apoptotic activity in primary mouse islet cells. Pal, palmitate. (C–E) Chronic FKN-Fc administration improves GSIS and decreases apoptosis in islets of HFD WT mice. 10 week HFD mice were treated with vehicle or FKN-Fc for an additional 8 weeks. Islets were isolated and similar sized islets were picked under the microscope and subjected to in vitro GSIS (C), quantitative RT-PCR (Q-PCR) (D) and caspase-3/7 activity assays (E). (F–G) Chronic FKN-Fc administration decreases β cell apoptosis in ob/ob mice. 8 week-old ob/ob mice were ip injected with vehicle or 30 mg/kg FKN-Fc every other day for 7 weeks. β cell apoptosis and apoptoic gene expression was assessed by immunohistochemistry (IHC) analyses using anti-insulin and anti-active (cleaved) caspase-3 antibodies (F) and Q-PCR (G), respectively. n = 4. (H and I) Morphometric analyses of HFD mouse islets. 10 week HFD mice were treated with FKN-Fc every other day for 8 weeks. A whole pancreas was harvested from each mouse, weighed and then fixed for IHC analyses. β Cell mass (H) and islet number per unit pancreatic area (I) were measured after staining with anti-insulin antibody, as described in Methods. Images are obtained at ×20 magnification. AU, arbitrary unit. For statistical analysis, 2-tailed paired t test (C, E, F, and H) or 1-way ANOVA (A, B, D, and G) was performed. In all graph panels, values are mean ± SEM and the symbols indicate statistical analysis: *P < 0.05 versus lane 1; **P < 0.01 versus lane 1; #P < 0.05 versus lane 2; ##P < 0.01 versus lane 2. See also Supplemental Figure 2.