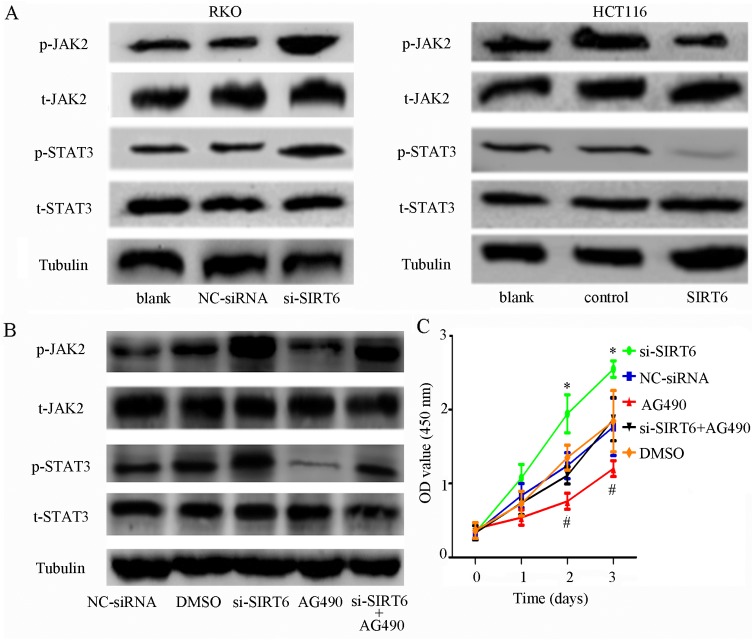
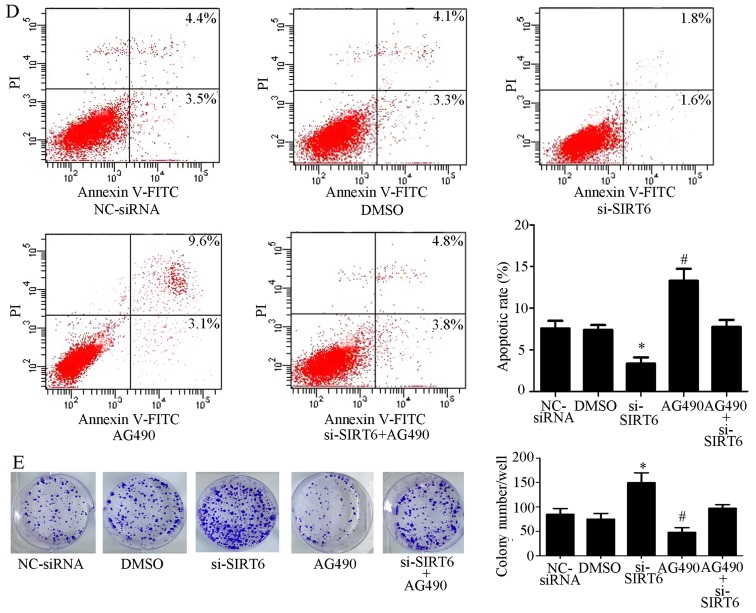
Figure 4.
SIRT6 overexpression inhibits the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in colon cancer cells. (A) Phosphorylation of JAK2 and STAT3 was increased in the si-SIRT6 group and inhibited in the SIRT6 group compared with the other groups. (B) Phosphorylation of JAK2 and STAT3 was activated by SIRT6 knockdown and inhibited by AG490 in RKO cell lines. However, transfection with si-SIRT6 abolished the effects of AG490, which further confirmed that SIRT6 may regulate the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways. (C) Proliferation rate was higher in the si-SIRT6 group and lower in the si-SIRT6 + AG490 group. The proliferation-inhibiting effects of AG490 were attenuated by si-SIRT6; *P<0.05, si-SIRT6 group vs. the other groups; #P<0.05, AG490 group vs. the other groups. (D) AG490 induced apoptosis of RKO cells, whereas si-SIRT6 exerted the opposite effect. However, the effects of AG490 were reversed by si-SIRT6; *P<0.05 vs. other groups; #P<0.05 vs other groups. (E) Colony-forming ability was increased by SIRT6 knockdown and decreased by AG490. The effects of AG490 could be eliminated by SIRT6 knockdown; *P<0.05 vs. the other groups; #P<0.05 vs. the other groups. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; JAK2, Janus kinase 2; NC, negative control; OD, optical density; p-, phosphorylated; PI, propidium iodide; si/siRNA, small interfering RNA; SIRT6, sirtuin 6; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; t, total.