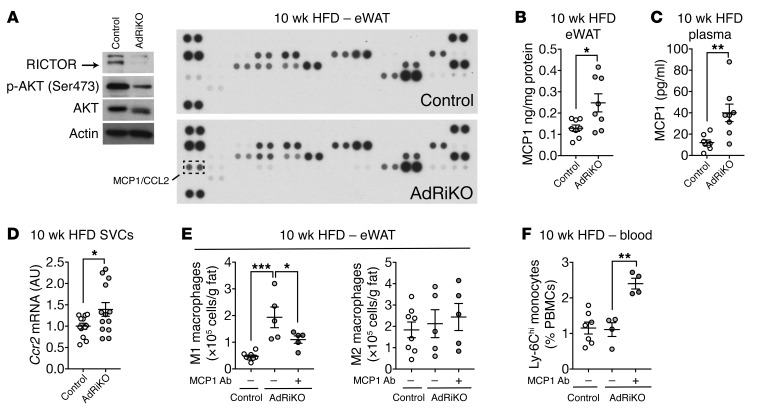
Figure 4. Insulin/mTORC2 signaling inhibits Mcp1 transcription and M1 macrophage accumulation in vivo.
(A) Adipokine array of eWAT from HFD-fed AdRiKO and control mice. Immunoblots show the reduction of RICTOR expression and mTORC2 signaling. n = 8 (data from 8 mice were pooled). (B) MCP1 protein levels in eWAT from HFD-fed AdRiKO and control mice. *P < 0.05, by unpaired Student’s t test. n = 8. (C) MCP1 protein levels in plasma from HFD-fed AdRiKO and control mice. **P < 0.01, by unpaired Student’s t test. n = 8. (D) Ccr2 mRNA levels in SVCs isolated from eWAT of HFD-fed AdRiKO and control mice. *P < 0.05, by unpaired Student’s t test. n = 12. (E) Numbers of M1 macrophages (CD45+F4/80+CD11b+CD11c+) and M2 macrophages (CD45+F4/80+CD11b+CD301+) in eWAT. Mice were fed a HFD for 8 weeks and treated with a control or MCP1-neutralizing antibody for 2 weeks with ongoing HFD feeding. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001, by 1-way ANOVA. n = 5–8. (F) Percentage of inflammatory monocytes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Mice were treated as in E. **P < 0.01, by 1-way ANOVA. n = 4–7. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM.