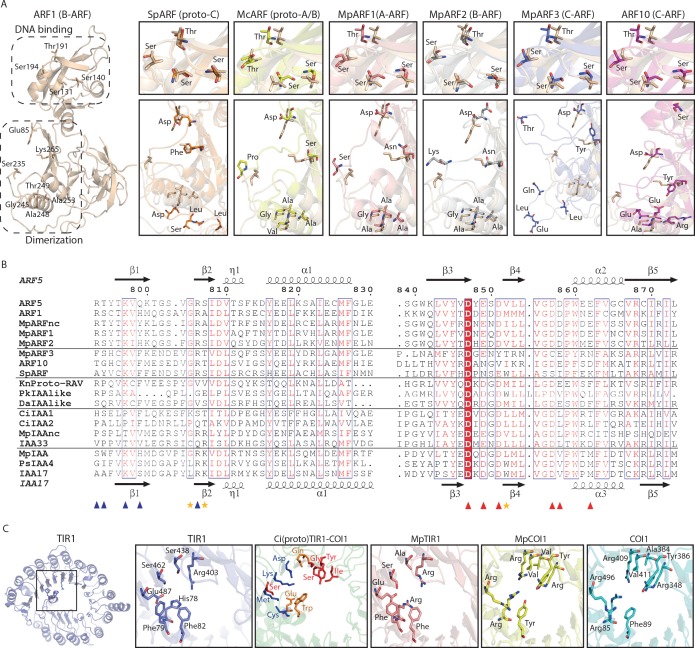
Figure 3. Homology models of ancestral ARF, Aux/IAA and TIR1/AFB proteins.
(A) Homology models for ARF DBDs. The crystal structure of Arabidopsis thaliana ARF1-DBD is shown on the left with important residues for DNA binding (top) and dimerization (bottom). Homology models for (proto-)ARFs are overlaid on A. thaliana ARF1 in right panels (brown). (B) Alignment of PB1 domain of (proto-)ARF, Aux/IAA and proto-RAV proteins. Numbering is based on the ARF5 protein of A. thaliana. Arrows and helices indicate β-sheets and α-helices in ARF5 and IAA17 of A.thaliana, respectively. Blue and red triangles indicate positive (+) and negative (-) faces, respectively. Golden asterisks represent the residues of polar interactions. (C) Homology models for TIR1/AFB and COI1 proteins. Left panel shows crystal structure of A. thaliana TIR1 from top view. Auxin-binding pocket of TIR1/AFB and jasmonate-binding pocket of COI1 are shown in right panels. Hormone-binding residues are indicated as stick model in TIR1 and COI1 of land plants. Blue, red or orange residues in the model for the Coleochaete irregularis protein indicate the residues aligned with hormone binding residues of TIR1, COI1 or both, respectively. Ci: Coloechaete irregularis, Da: Desmidium aptogonum, Kn: Klebsormidium nitens, Mc: Mesotaenium caldariorum, Mp: Marchantia polymorpha, Pk: Parachlorella kessleri, Ps: Pisum sativum, Sp: Spirogyra pratensis.