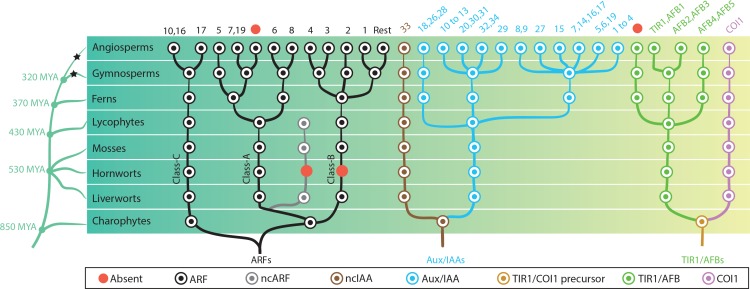
Figure 4. Reconstruction of ancestral state of NAP components in plant evolution.
Phylogeny of taxonomic classes are shown in left. Time point of the lineage diversification was calculated using TimeTree database (Kumar et al., 2017). Black stars indicate whole genome duplication events (Jiao et al., 2011). Right: phylogenetic trees show the copy number and phylogenetic relationship of each protein family in the common ancestors. Each circle is colored according to protein type as indicated in the box. In the top row, numbers indicate which genes of Arabidopsis thaliana belong to each subfamily and red circles indicates missing subfamilies in A. thaliana. Note that only branches with strong bootstrap support are shown.