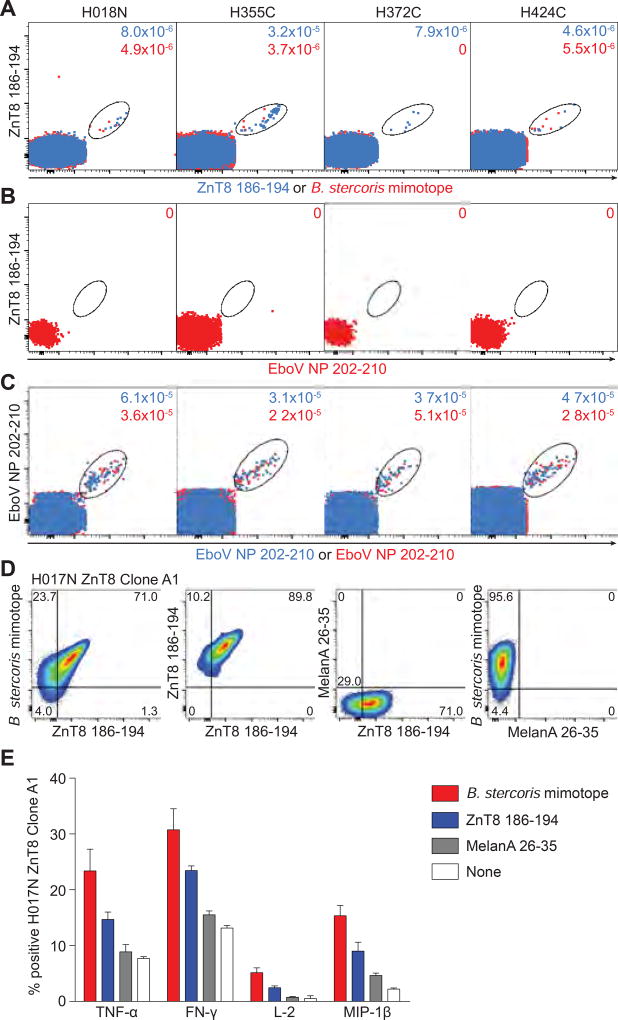
Fig. 7. ZnT8186–194-reactive CD8+ T cells cross-recognize a B. stercoris mimotope.
(A–C) Four donors with sizable ZnT8186–194 MMr+CD8+ T-cell fractions were selected. A first PBMC aliquot received PE/BV786-labeled ZnT8186–194 MMrs and PE/BV711-labeled EboV NP202–210 MMrs. For the second aliquot, PE-labeled B. stercoris MMrs replaced the PE-labeled ZnT8186–194 MMrs. (A) Overlay of ZnT8186–194/ZnT8186–194 MMr+ (blue) and ZnT8186–194/B. stercoris MMr+ cells (red). (B) Negative control staining of ZnT8186–194/EboV NP202–210 MMr+ cells. (C) Positive control staining of EboV NP202–210/EboV NP202–210 MMr+ cells from the first and second aliquot. The frequencies of MMr+ out of total CD8+ T cells are indicated. (D) Four ZnT8186–194-reactive CD8+ T-cell clones (D222D 2, D349D 178B9, H017N A1, H328C 9C8) were stained with BV786/PE-labeled ZnT8186–194, PE-labeled B. stercoris and BV650-labeled MelanA26–35 MMrs. The ZnT8186–194/B. stercoris cross-reactive clone H017N is shown, from left to right: ZnT8186–194/B. stercoris MMr+; ZnT8186–194/ZnT8186–194 MMr+; and negative control ZnT8186–194/MelanA26–35 and B. stercoris/MelanA26–35 MMr+ cells. (E) The H017N clone was stimulated with peptide-pulsed LCLs (0.1 µM, 6 h). Percent cytokine+ cells are shown as mean±SEM of two experiments. p=0.008 for Wilcoxon signed-rank comparison of pooled cytokine responses between B. stercoris and ZnT8186–194, MelanA26–35 or no peptide, and between ZnT8186–194 and MelanA26–35 or no peptide.