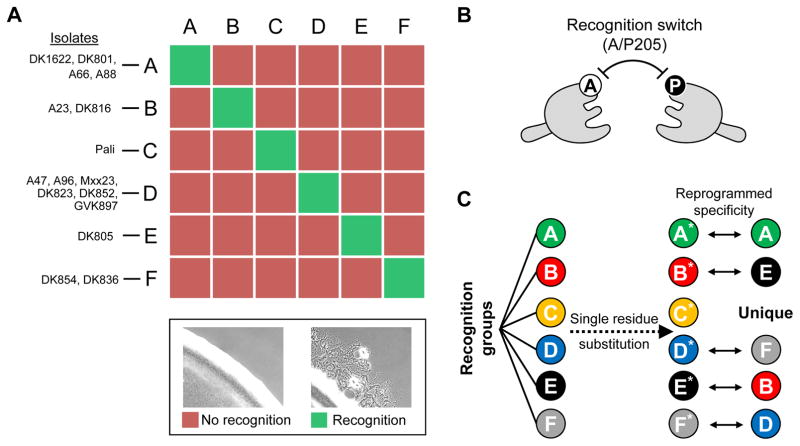
Fig. 2. TraA recognition in myxobacteria.
A) 16 M. xanthus environmental isolates form six distinct recognition groups. Members of each group are shown. Representative micrographs of experimental assay that determines TraA recognition specificity is shown (bottom). In brief, TraA cell-cell recognition between two strains results in motility (flares) at the edge of a mixed colony(Pathak et al., 2013). B) Single amino acid substitutions in a TraA (A/P205) switch leads to a change in homotypic recognition specificity between receptors (Cao & Wall, 2017). C) TraA homotypic recognition reprogrammed through single residue substitutions (A205P or P205A) from six recognition groups. TraA receptors after A/P substitutions are indicated with asterisks, and their recognition specificities are shown on the right.