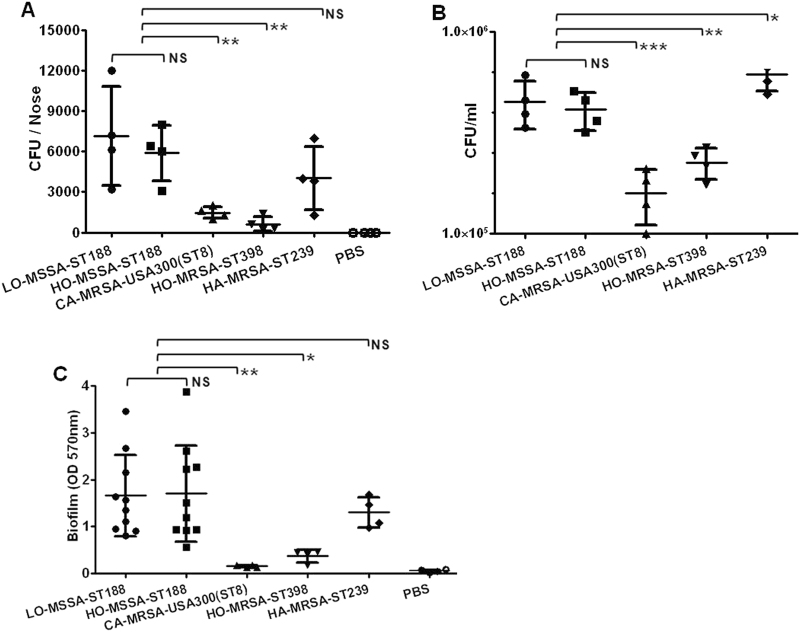
Fig. 4. Nasal colonization, cell adhesion, and biofilm formation ability of host-adapted S. aureus ST188.
a The nasal colonization ability of ST188 in mice was compared with that of CA-MRSA USA300 (ST8), HO-MRSA ST398 and HA-MRSA ST239 (4 isolates were randomly selected/lineage). Each mouse (one mouse/isolate) received 1 × 108 colony-forming units (CFUs) in the nares. Control animals (n = 4) received only sterile PBS. b Adhesion of S. aureus to human alveolar epithelial cells A549. Colony counts of adhesive and internalized bacteria on/in A549 epithelial cells after infection. Control group (n = 4) received only sterile PBS. c Semiquantitative biofilm assays demonstrating the biofilm formation ability of ST188 isolates (10 isolates were randomly selected). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; NS, not significant (P ≥ 0.05). LO livestock-originated, HO human-originated