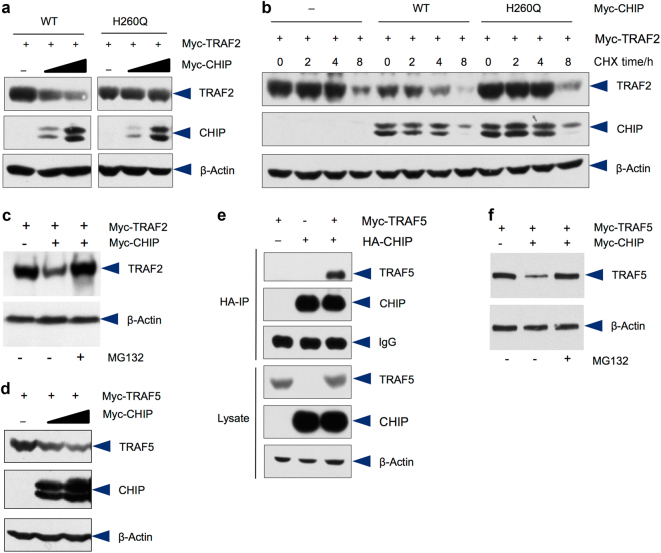
Fig. 4.
CHIP promotes TRAF2 and TRAF5 degradation. a CHIP promotes T RAF2 degradation. Myc-TRAF2 was co-transfected with increasing concentrations of Myc-CHIP or mutant Myc-CHIP (H260Q) in 293 T cells. 24 h after transfection, the cell lysates were collected and samples were subjected to Western blot analysis. TRAF2 protein levels were decreased when cells were transfected with increasing concentrations of CHIP expression plasmid. b 293 T cells were transfected with TRAF2 and WT or mutant CHIP expression plasmids and treated with cycloheximide (CHX) for different periods of time as indicated. Transfection of WT CHIP, but not mutant CHIP, accelerated TRAF2 degradation. c TRAF2 was transfected with or without CHIP in 293 T cells. Steady state protein levels of TRAF2 were reduced by co-transfection with CHIP. The CHIP-mediated TRAF2 degradation was inhibited by the treatment with proteasome inhibitor MG-132. d Myc-TRAF5 and increasing concentrations Myc-CHIP expression plasmids were co-transfected into 293 T cells. CHIP promoted TRAF5 degradation. e HA-CHIP and Myc-TRAF5 were co-transfected into 293 T cells. Cell lysates were incubated with the anti-HA antibody and immunoprecipitates were then subjected to Western blot analysis. The results showed that TRAF5 interacts with CHIP. f TRAF5 was transfected with or without CHIP in 293 T cells. Steady state protein levels of TRAF5 were reduced by co-transfection with CHIP. The CHIP-mediated TRAF5 degradation was inhibited by the treatment with proteasome inhibitor MG-132.