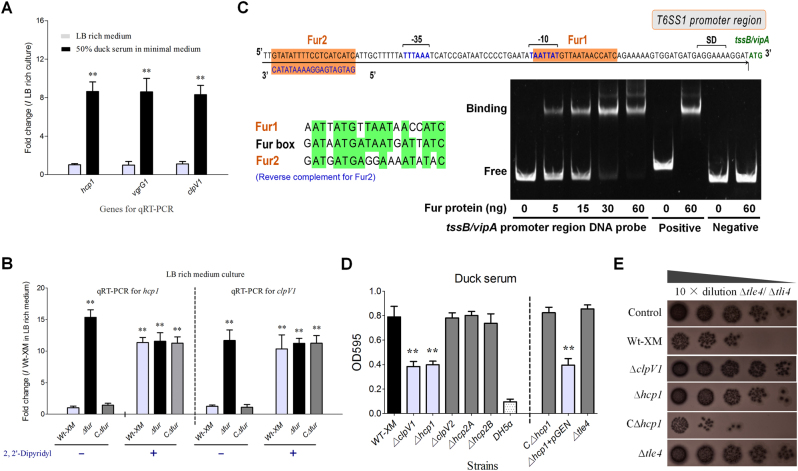
Fig. 2. Transcriptional regulation and functional identification of the hcp1 cluster.
a The 50% duck serum in minimal medium could activate hcp1 and vgrG1 transcription. b The APEC T6SS1 gene cluster was regulated by the iron concentration and the Fur repressor. a, b Gene expression in the indicted conditions was analyzed by qRT-PCR. Expression levels were normalized against the level of the housekeeping gene tus. The relative expression levels are presented as the means ± SD obtained from three independently isolated RNA samples. c Fur directly regulated the T6SS1 operon. An in silico analysis was performed for the T6SS1 proximal promoter region. The ATG codon of tssB/vipA and the Shine-Dalgarno sequence (SD) are indicated. The putative −10 and −35 elements of the promoter (identified using the BProm program SoftBerry) are indicated in blue, and Fur-binding sequences are shown in orange boxes. In the nonradioactive EMSA assay of Fur, fepA promoter region DNA probes with and without Fur protein were used as positive controls, and tssB/vipA coding region DNA probes with and without the Fur protein were used as negative controls. d Hcp1 was involved in biofilm formation. The biofilm assay was performed using the 1% crystal violet method, **p < 0.01. Error bars represent the standard deviation for three independent experiments. e Hcp1 was required for the antibacterial activity of Tle4 against unprotected sister cells. The Tle4/Tli4 effector/immunity pair has been identified in our previous study6. The donor and recipient strains were mixed at a ratio of 3:1 and incubated for 6 h at 30 °C. Plate growth was demonstrated on NalR eosin-methylene blue agar, and the bacterial plaques (induced NalR) represent increasing serial 10-fold dilutions from left to right