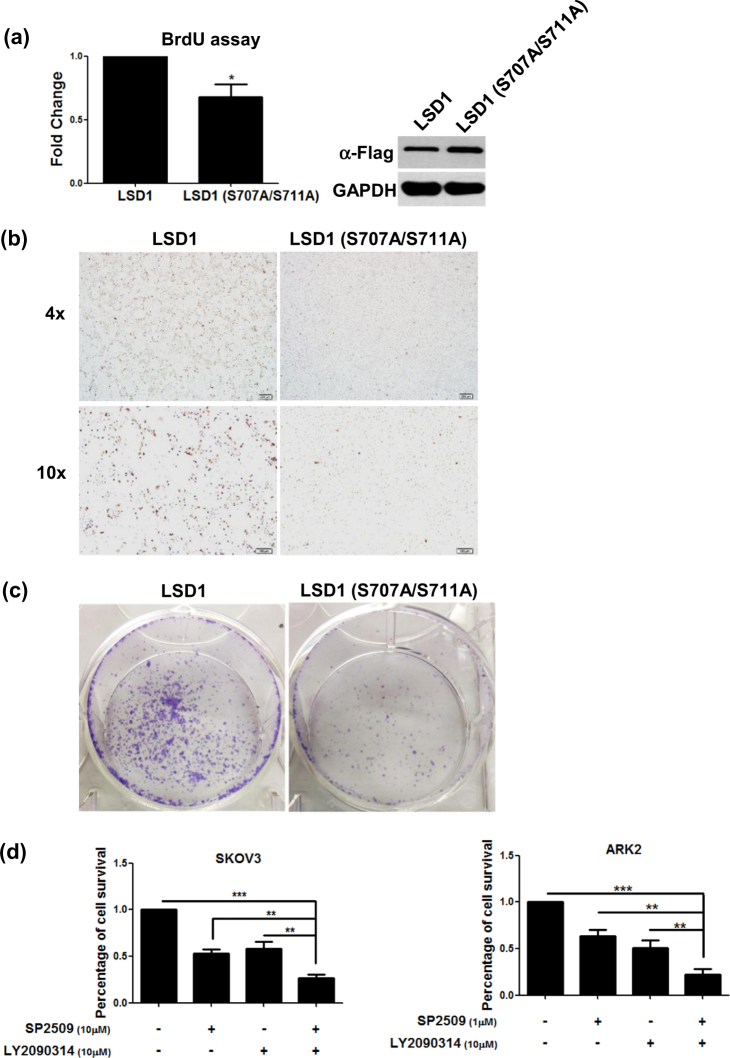
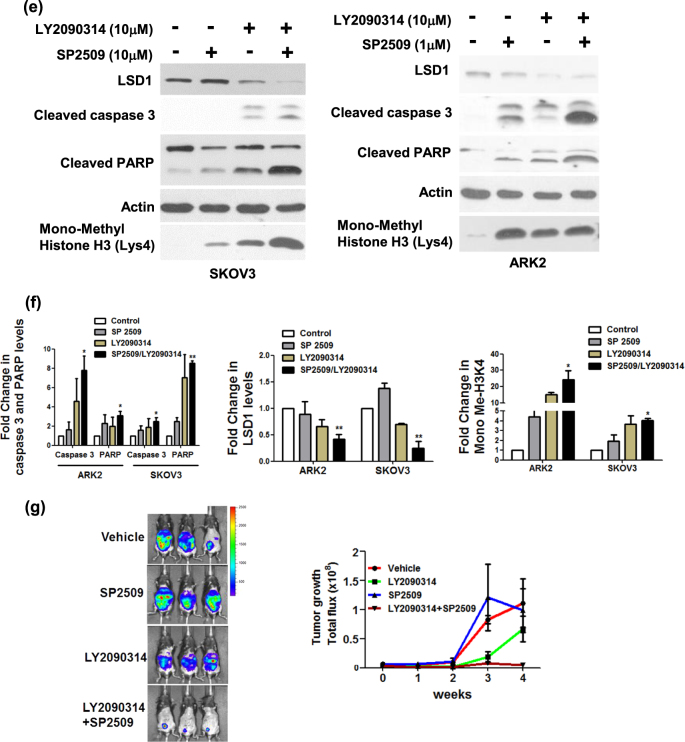
Fig. 5. The combination of the LSD1 inhibitor SP2509 and the GSK3β inhibitor LY2090314 exerts synergistic antitumor effects.
a BrdU proliferation assay, b Ki67 protein immunostaining, and c colony formation assay in ARK2 cells (1000 cells cultured in 1% FBS medium in 6-well plate) stably expressing Flag-wild-type LSD1 or Flag-double-mutant (S707A/S711A) LSD1. d SKOV3 and ARK2 cells were treated with the reported concentrations of SP2509, LY2090314, or a combination of SP2509 and LY2090314 for 72 h. Cell survival was determined with the MTT assay. e Exposure of SKOV3 and ARK2 cells to a combination of SP2509 and LY2090314 for 72 h increased apoptosis (as reflected by higher levels of cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved PARP quantified by Western blot). LSD1 activity was assessed by measuring protein levels of mono-methylated histone H3K4. Actin levels were used to normalize input proteins. f Quantified results from e were obtained from three independent experiments and are presented as mean ± standard error (SE). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Student’s t-test. g Mosec/Luc cells (1 × 106) were intraperitoneally injected into C57BL/6 mice. One week later, mice were injected with vehicle alone, LY2090314 (10 mg/kg), SP2509 (10 mg/kg), or both twice a week. Tumor growth was measured on a weekly basis after treatment was started. Ascites were detected in mice treated with vehicle alone or SP2509. The mice were then analyzed with the IVIS Spectrum in vivo imaging system on a weekly basis. Data are expressed as means ± standard error