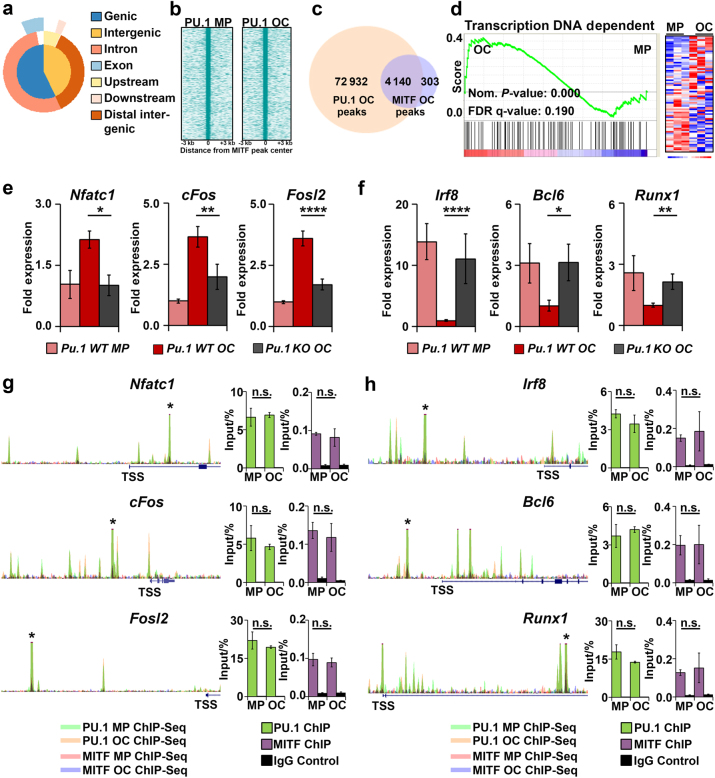
Fig. 4.
PU.1 and its co-partner MITF regulate the expression of a network of TFs necessary for OC differentiation. a Graphical representation of the distribution of MITF OC ChIP-Seq peaks throughout the genome. b Treeview plot of genome-wide PU.1 MP and PU.1 OC ChIP-Seq tags ± 3 000 base pairs from MITF MP or MITF OC peak centers. c Venn diagram depicting the OC ChIP-Seq peak sites shared between PU.1 and MITF. d GSEA plot of a TF gene set significantly enriched in genes with overlapping PU.1 and MITF OC ChIP-Seq peaks using our murine MP and OC microarray data (n = 3). Heatmap (right) indicating MP and OC expression of genes in the gene list. e RT-qPCR analysis of 3 TFs on the GSEA gene list, which are necessary for OC differentiation. Gene expression is shown for WT MPs and OCs and Pu.1 KO OCs (n = 3). f RT-qPCR analysis of 3 TFs on the GSEA gene list which inhibit OC differentiation. Gene expression is shown for WT MPs and OCs and Pu.1 KO OCs (n = 3). g, h Depiction of MP and OC PU.1 and MITF ChIP-Seq peaks near the TF loci analyzed in e and f. Each trace is 30 kb wide and the TSS is indicated. Conventional ChIP validation of PU.1 and MITF binding to the starred sites is shown (bar graphs, n = 3).