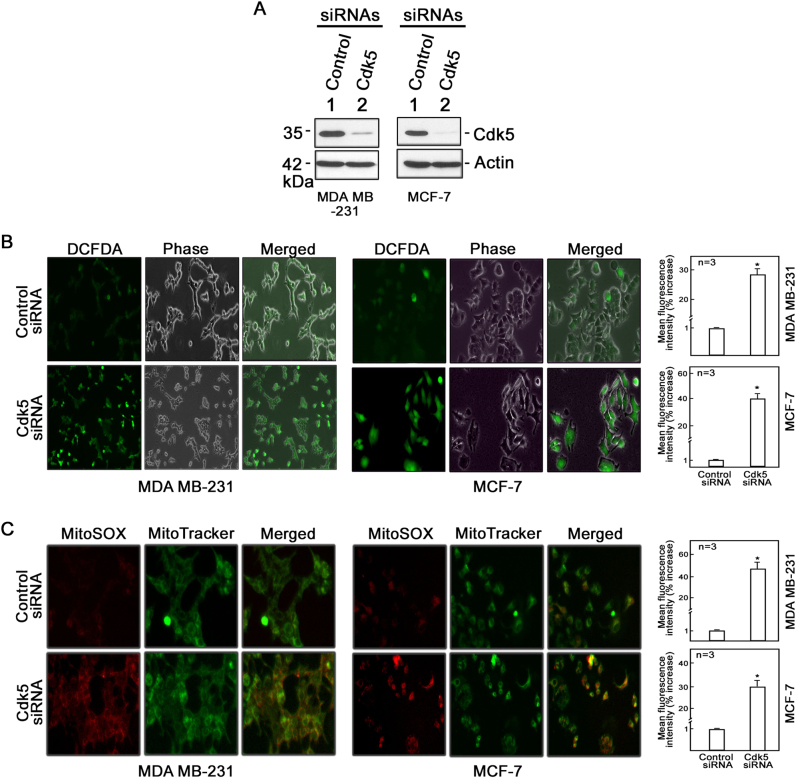
Fig. 1.
Loss of Cdk5 in breast cancer cells causes a dramatic increase in production of cytoplasmic hydrogen peroxide and mitochondrial superoxide anions. a Cdk5 silencing in MDA MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Following transfection with Cdk5 siRNA (100 nM) for 72 h, cells were lysed and subjected to immunoblotting using a Cdk5 antibody. Blot shown represents one of three blots with similar patterns. Actin blot serves as loading control. b Cytoplasmic hydrogen peroxide and c mitochondrial superoxide levels were assessed in MDA MB-231 (left panel) and MCF-7 (right panel) cells depleted of Cdk5. After 72-h transfection with Cdk5 siRNA, cells were stained with DCFDA (5 µM) or MitoSOX red (5 µM), and MitoTracker green (200 nM) for 30 min to measure cytoplasmic hydrogen peroxide and mitochondrial superoxide anions, respectively, by fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. Cell images were acquired using an Olympus 1 × 71 microscope at ×160 magnification. The graphs in (b) and (c) represent % increase in mean fluorescence intensity over the control siRNA-transfected cells as analyzed by flow cytometry. All values are means ± SEM from triplicate experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using a Student’s t-test (unpaired). * indicates statistically significant difference at p < 0.05