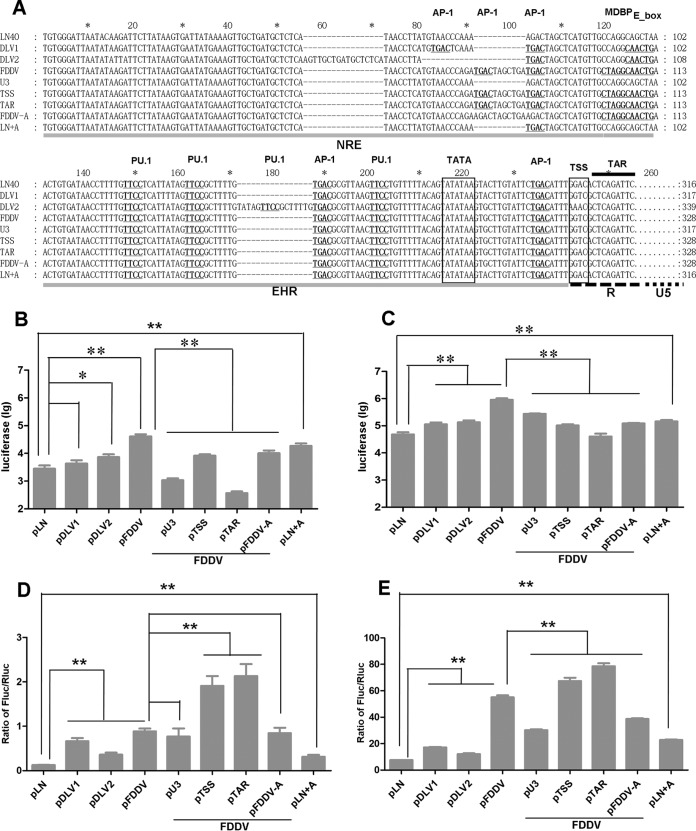
FIG 6.
Effects of LTR mutations on the promoter activities of reporter genes in vitro. (A) Comparison of the different LTR variant sequences for which reporter luciferase gene plasmids were constructed. The luciferase reporter viruses were used to infect eMDMs without (B) or with (C) coinfection with DLV121 (for the provision of Tat). After 48 h, the cells were lysed, and the promoter activity of each LTR variant was examined. FDD cells were cotransfected with the pGL-LTRs, pRL-CMV vector, and pcDNA3.1 (D) or pTat (E). The cells were lysed 48 h posttransfection, and the firefly luciferase (Fluc) and Renilla luciferase (Rluc) activities were assayed. LN, derived from the LN40 LTR sequence, was used as the reference sequence. DLV1 was derived from DLV121; compared with the LN sequence, the NRE region of DLV1 has two additional AP-1 binding sites, the EHR has an additional E-box binding site, TSS is mutated to GGTC, and the TAR initiation site is mutated to G. DLV2 was derived from DLV121; compared with the LN sequence, its U3 region has two insertion mutations in positions 56 to 72 and 179 to 194 and a deletion mutation in positions 82 to 92, its NRE has an additional AP-1 binding site, the EHR has one additional E-box binding site, the TSS is mutated to GGTC, and the TAR initiation site is mutated to G. FDDV was derived from FDDV13; compared with the LN sequence, its NRE has an additional 11-bp repetitive sequence in positions 93 to 103 and two AP-1 binding sites, its EHR has one additional MDBP and one additional E-box binding site, the TSS is mutated to GGTC, and the TAR initiation site is mutated to G. U3 was based on FDDV, with the U3 region replaced with the LN sequence. TSS was based on FDDV, with the TSS mutated from GGTC to GGAC. TAR was based on FDDV, with the TAR start site mutated from G to A. FDDV-A was based on FDDV, with the 75T/A and 86T/A mutations and the absence of the two AP-1 binding sites in the NRE. LN+A was based on LN with the 75A/T mutation and the addition of one AP-1 binding site.