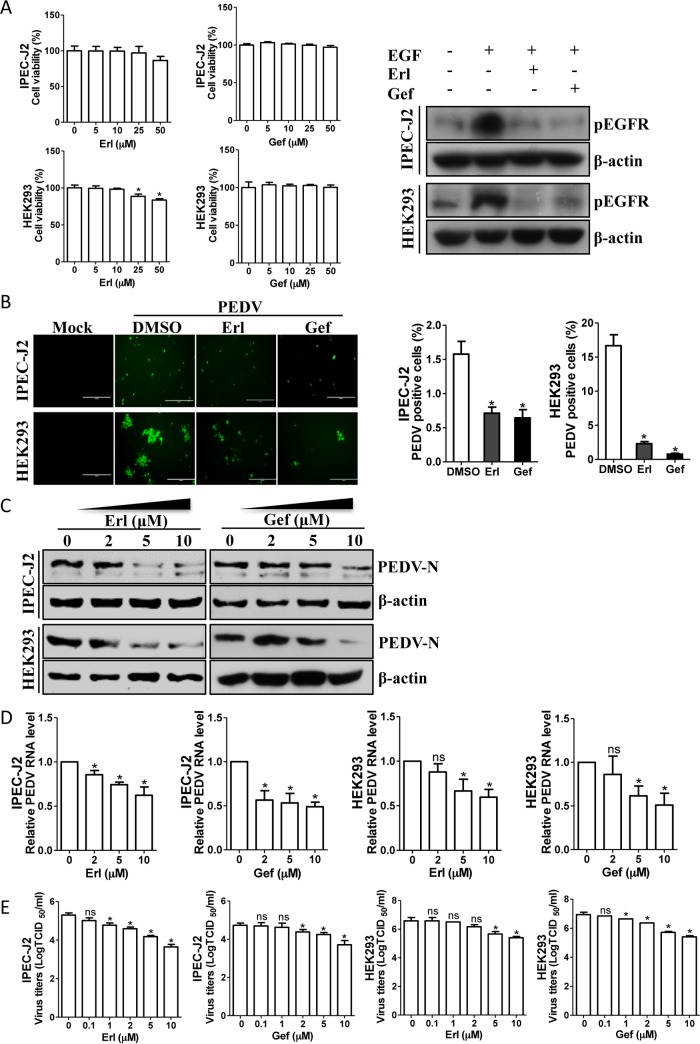
FIG 4.
EGFR inhibitors reduce PEDV infection. (A) Effects of inhibitors on EGFR function. IPEC-J2 and HEK293 cells were treated with the carrier control DMSO or EGFR-specific inhibitors, erlotinib (Erl) and gefitinib (Gef), at different concentrations for 72 h. Cell cytotoxicity was analyzed with the CCK-8 system as described in Materials and Methods. IPEC-J2 and HEK293 cells were also pretreated with an EGFR-specific inhibitor, Erl or Gef, at 10 μM or with DMSO for 12 h, followed by EGF stimulation (10 ng/ml) for 15 min. The levels of pEGFR and β-actin were analyzed by Western blotting. (B) EGFR inhibitors decrease the number of PEDV-positive cells. IPEC-J2 and HEK293 cells were pretreated with DMSO or EGFR inhibitors, Erl and Gef, at 10 μM for 12 h. After washing, the cells were infected with PEDV or mock control in the absence or presence of inhibitors. At 48 hpi or 24 hpi, the cell monolayers were fixed and examined for PEDV infection by IFA with an anti-PEDV spike protein MAb (3F12). The number of PEDV-positive cells was calculated. (C) Reduction of PEDV N protein by EGFR inhibitors is concentration dependent. Detergent lysates collected from IPEC-J2 and HEK293 cells were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies as indicated. (D) EGFR inhibitors decreased PEDV RNA levels, as determined by quantitative RT-PCR. (E) Virus titers were reduced after inhibitor treatment, as detected by TCID50 assay. The results are representative of three independent experiments (means and SD). *, P < 0.05; ns, not significant. The P value was calculated using Student's t test.