FIG 8.
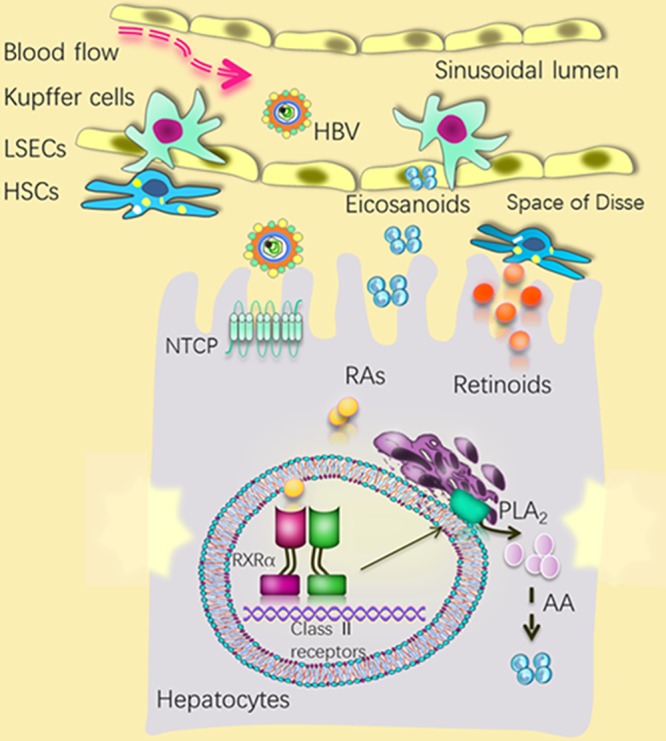
A speculative scheme for the role of hepatic RXRα and related metabolic homeostasis in modulating HBV infection within the liver microenvironment. Silencing RXRα in hepatocytes enhanced HBV infection at early stages, whereas activation of RXRα by natural ligands (e.g., retinoic acid) inhibited HBV infection at early stages. Altered retinoid homeostasis during HSC activation and increased production of eicosanoids (from Kupffer cells) in a response to various inflammatory stimuli, such as HBV infection, may affect HBV infection. LSECs, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells.
